The Bradshaw Model is a geographical model that shows how the characteristics of a river change as it moves downstream from its source to its mouth. It helps explain patterns in river width, depth, velocity, discharge and sediment size.
What Is the Bradshaw Model?
The Bradshaw Model illustrates downstream changes in a river by comparing different variables along the river’s course.
It shows that as the distance downstream increases:
- The river becomes larger and more efficient
- The amount of water increases
- The river’s energy and ability to transport material change
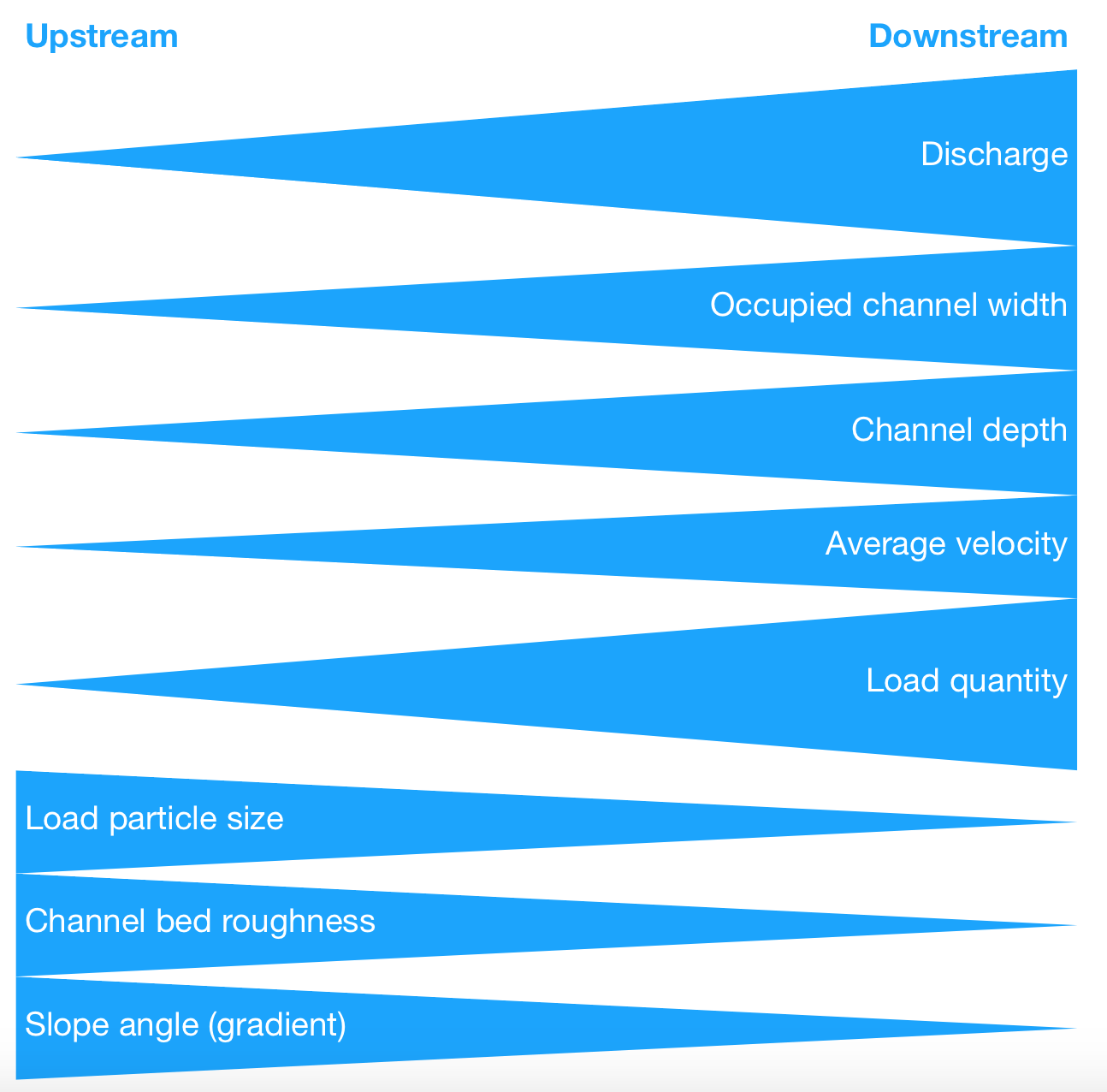
The Bradshaw Model
The model is based on observations of real rivers, but it is simplified; not all rivers follow it perfectly.
Key Changes Shown by the Bradshaw Model
Channel Width
- Narrow near the source
- Becomes progressively wider downstream
- Caused by increased erosion and higher discharge
Channel Depth
- Shallow in the upper course
- Increases downstream
- Deeper channels reduce friction, allowing faster flow
Velocity (Speed of Flow)
- Slower near the source due to rough channels and high friction
- Increases downstream as the channel becomes smoother and deeper
- Less friction relative to the volume of water
Discharge
- Low near the source
- Increases downstream as tributaries add water
- Measured in cubic metres per second (m³/s)
Sediment Size and Shape
- Large, angular material near the source
- Sediment becomes smaller, rounder and smoother downstream
- Due to attrition and abrasion
Why Do These Changes Happen?
Downstream changes occur because:
- More tributaries join the river, increasing discharge
- The river has more energy to erode laterally
- Bedload collisions reduce sediment size
- The channel becomes smoother and more efficient
Strengths of the Bradshaw Model
- Clearly shows patterns of change downstream
- Useful for exam explanations
- Helps link river processes to river characteristics
Limitations of the Bradshaw Model
- Rivers may be altered by human activities (e.g. dams, straightening)
- Geology and climate can cause rivers to behave differently
- Not all rivers show a smooth, continuous pattern of change
Using the Bradshaw Model in Exams
When answering exam questions:
- Refer to distance downstream
- Use comparative language (e.g. increases, decreases)
- Link changes to processes such as erosion, friction and tributaries
- Acknowledge that it is a generalised model
