Lombok Indonesia Earthquake 2018 Case Study
The causes, effects, and responses to the Lombok earthquake
Lombok is one of the 17508 islands that make up Indonesia. The island is approximately 4,500 sq km (1,700 sq miles) and is located to the east of Bali and west of Sumbawa part of the Lesser Sunda Island chain. It’s known for beaches and surfing spots, particularly at Kuta and Banko Banko (in south Lombok).
In the first in the series, on 29 July, a 6.4 magnitude quake triggered landslides in the mountain region of the island and killed at least 16 people. Following this a shallow, magnitude 6.9 earthquake struck Lombok and Bali on August 5th, 2018, killing over 555 people, injuring 1300 and leaving at least 353000 homeless. The most severe damage was in North Lombok close to the epicentre.
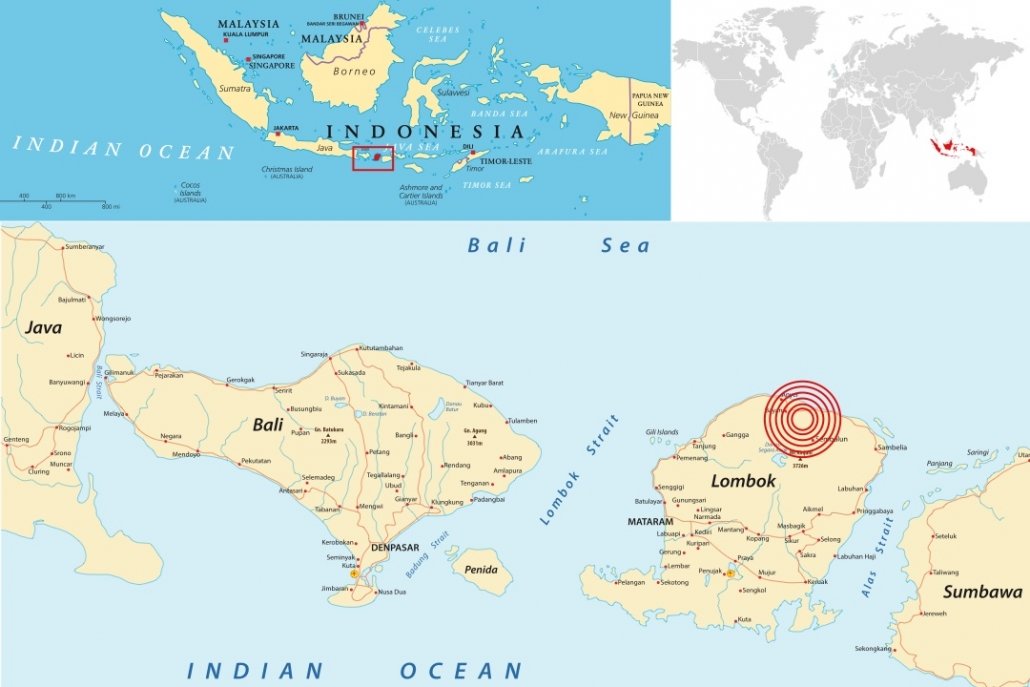
Location of the August 5th 2018 Lombok earthquake
The main quake struck at 19:46 local time (11:46 GMT) on Sunday, August 5th at a fairly shallow depth of 31km (19 miles).
Earthquakes are common in Indonesia because it lies on the Ring of Fire – the line of frequent quakes and volcanic eruptions that circles virtually the entire Pacific Rim.
More than half of the world’s active volcanoes above sea level are part of the ring.
The recent earthquakes have occurred along a specific zone where the Australian tectonic plate meets the Indonesian island plate, Sunda.
Tectonic plates are slabs of the Earth’s crust that move very slowly over our planet’s surface. Indonesia sits along the “Pacific Ring of Fire” where several tectonic plates collide and many volcanic eruptions and earthquakes occur.
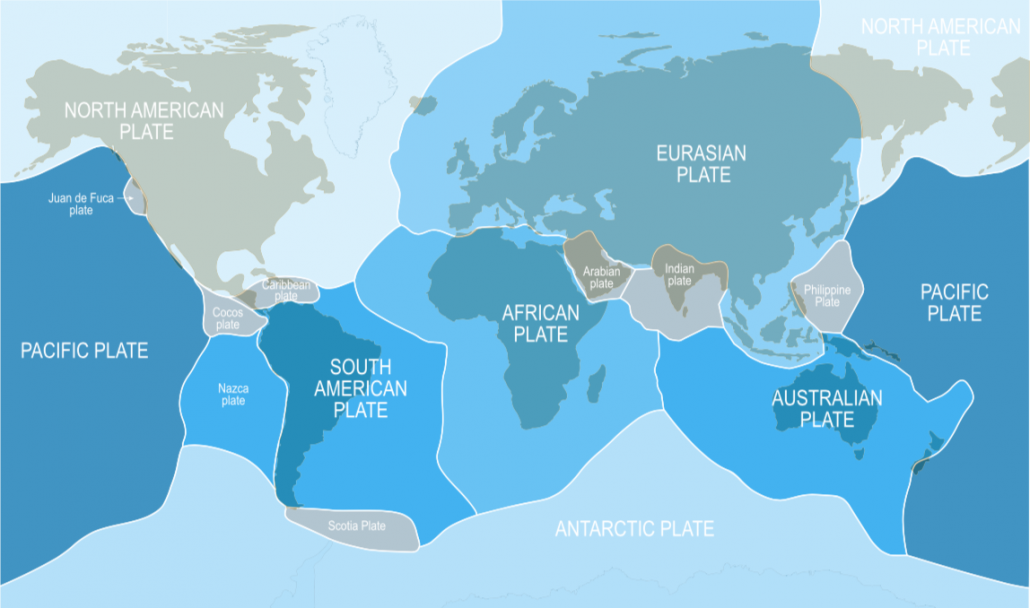
The Earth’s tectonic plates
Some of these earthquakes are very large, such as the magnitude 9.1 earthquake off the west coast of Sumatra that generated the 2004 Indian Ocean tsunami. This earthquake occurred along the Java-Sumatra subduction zone, where the Australian tectonic plate moves underneath Indonesia’s Sunda plate.
Both earthquakes occurred along faults in an area where tectonic plates are colliding, with one diving beneath the other.
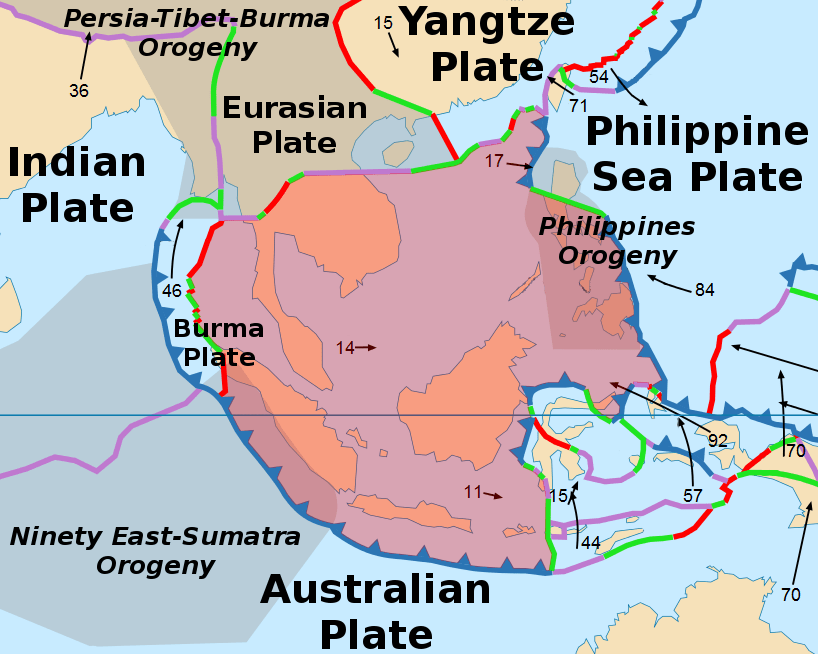
The Sunda Plate
In this area, there’s subduction, so the Australian plate is moving under the Sunda plate, and the Australian plate is moving to the north underneath the Sunda plate.
The earthquake destroyed tens of thousands of homes, mosques and businesses across Lombok on August 5 2018. More than 1,300 people were injured and nearly 353,000 have been internally displaced.
It is estimated that 80% of the region had been damaged by the earthquake. Lombok suffered more than 5 trillion rupiah ($342 million; £268 million) in damage following the 5 August earthquake, authorities said.
Hundreds of tourists were stranded on the island and hotels were filled to capacity. No tourists were reported killed, but the earthquake was felt as far away as the neighbouring island of Bali, where two people died. The quake was followed by more than a dozen aftershocks, with one registering magnitude 5.4 on the Richter Scale.
According to scientists from NASA and the California Institute of Technology’s rapid-imaging project, the earthquake lifted the island as much as 25 centimetres in some areas. In other places, the ground dropped five-15cm.
Emergency teams in East and North Lombok reported that in some villages 75% of homes were damaged.
More than 500 hikers, most of whom were foreigners, were stranded on Indonesia’s Mt Rinjani when a deadly quake triggered landslides. The earthquake triggered landslides around Mount Rinjani, cutting off escape routes. The volcano, which rises 3,726m (12,224ft) above sea level and is the second-highest one in Indonesia, is a favourite among sightseers.
The region was hit by more than 350 aftershocks. Some measured up to 6.2 on the Richter Scale and brought down some buildings.
The area around Mount Rinjani increasingly relies on tourism, the earthquake and aftershocks led to the closure of mountain to hikers leading to many hotel cancellations by international tourists.
Hundreds of British citizens and European citizens were stuck in Lombok airport before flights could resume.
Aftershocks killed at least a further 13 people as the region recovered from the main event.
The Indonesia Government declared a three-week long state of emergency. “The most important thing is the emergency response, after that rehabilitation and reconstruction,” said Indonesia’s second-in-command, Vice President Jusuf Kalla. The government mobilised the National Disaster Mitigation Agency (BNPB) and the national military, directly deploying personnel in response to the earthquake.
Two helicopters were deployed to assist in emergency operations and the military sent troops and medical personnel, as well as medical supplies and communications equipment. Five planes carrying food, medicine, blankets, field tents and water tankers left the capital, Jakarta, for the island early on Wednesday 8th August.
Supplies for those made homeless were distributed with about 30,000 tents and 100 wheelchairs sent to affected areas.
As hospitals and clinics were affected by the earthquake many of the injured were treated in the open air or in makeshift clinics.
Rescue efforts were hampered by power outages, a lack of phone reception in some areas and limited evacuation options. A lack of heavy lifting equipment also affected the relief effort, with some rescuers forced to dig by hand. Other obstacles in the mountainous north and east of Lombok included collapsed bridges and electricity and communication blackouts. Debris blocked damaged roads.
In Sembalun the community pulled together to repair damaged buildings, including the town’s only health clinic. Electricity and clean water had to be being restored to villages in Sambalia that were cut off.
Emergency workers gradually reached more remote areas of Lombok having focussed their initial efforts in urban areas.
More than 500 hikers who were stranded on a mountain on the Indonesian island of Lombok after the earthquake were safely evacuated. Most of the hikers and guides were able to walk down after a safe route was found for them but some were flown out by helicopter.
The UK Foreign Office worked with the Indonesian authorities to provide assistance to British people caught up in the earthquake. Extra flights were added to help people who want to leave Lombok. Airport authorities requested that additional flights be added on Monday 6th August 2018 , to accommodate the influx of tourists trying to leave the island.
Charity, Plan International, provided counselling for children and supported those who were unable to go to school, by distributing emergency school kits and helping teachers continue educating while schools remain closed. The charity also provided humanitarian assistance to 2,500 families in six villages in Lombok. The organisation dispatched 500 emergency shelter kits, containing 1,000 tarpaulins, 1,000 sleeping mats and 2,000 blankets.
The Salvation Army in Indonesia also provided medical and other assistance to people who were affected by the earthquake on Lombok. The team immediately distributed a small supply of rice, noodles, sugar and bottled water to the affected population.
The Indonesian Red Cross (Palang Merah Indonesia) disaster responders provided first aid and assessed immediate needs in remote villages, arranging for bottled water and rice to be delivered by motorbike.
British-based charity Oxfam said it was providing clean drinking water and tarpaulin shelter sheets to 5,000 people and planned to intensify aid delivery.
A French military transport plane delivered 25 tonnes of humanitarian aid to the earthquake-hit island of Lombok on behalf of the Indonesian government.
On the 14th August 2018, The EU announced a further €500 000 to step up its emergency response to meet the most pressing needs of those affected by the devastating earthquakes that struck the Indonesian island of Lombok in late July and early August. The allocation came in addition to the initial €150 000 delivered earlier in August, thus bringing the EU’s contribution to €650 000. The EU humanitarian funding complemented the Indonesian government response and focussed on the most vulnerable groups and communities in the affected area. The EU aid supported the International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies (IFRC) in providing relief assistance and protection to the most vulnerable among the affected population. It is estimated that the aid directly benefited 80 000 vulnerable people in some of the worst hit localities in the northeast and west Lombok districts. The aid was also used to assist the IFRC in reuniting families that were separated by the earthquakes. Aid was also offered by other countries including Australia.
Allegedly, authorities on Lombok were demanding money from tourists before they would let them onto rescue boats. However, around 5000 tourists who wanted to be evacuated from three outlying holiday islands had left by boat.
Use the images below to explore related GeoTopics.