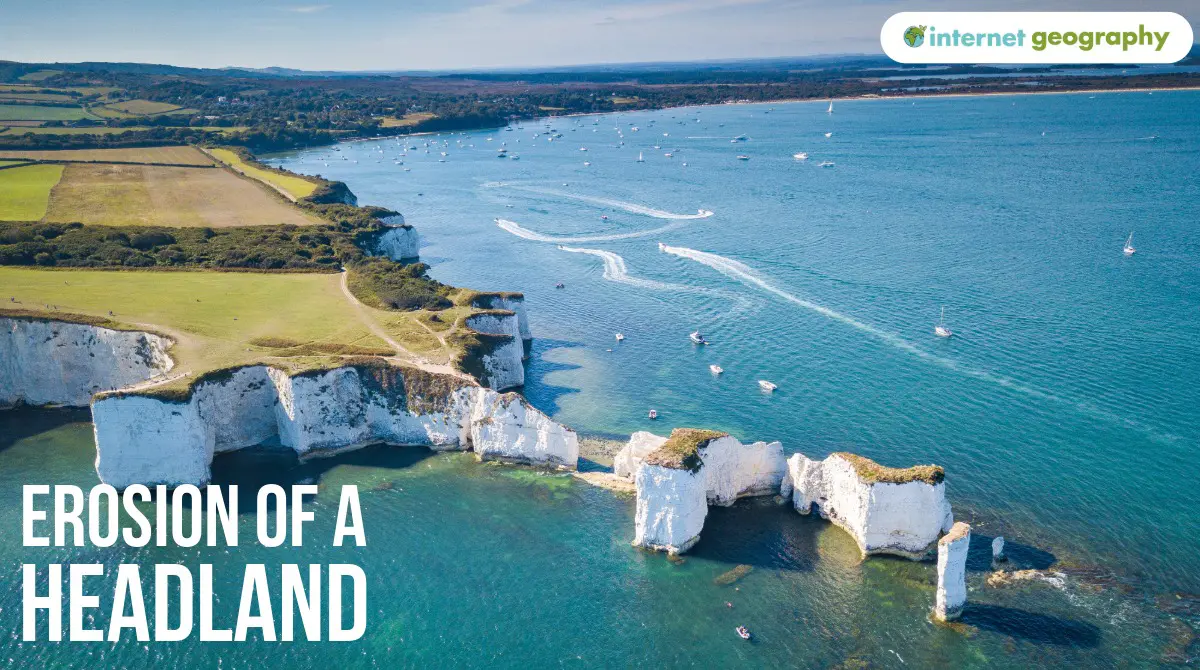
Erosion of a headland
A headland is an area of hard rock that sticks out into the sea. Headlands form in areas of alternating hard and soft rock. Where the soft rock is eroded, bays form on either side of the headland. As the headland becomes more exposed to the wind and waves, the rate of erosion increases. When headlands erode, they create distinct features such as caves, arches, stacks and stumps.
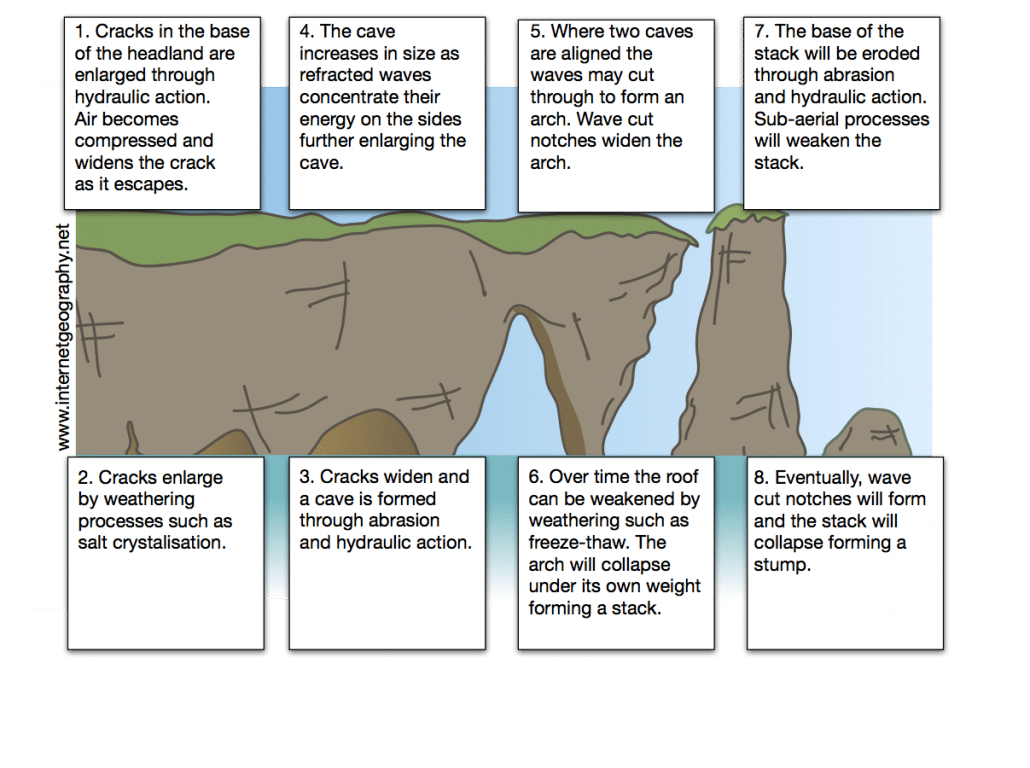
The diagram below shows the sequence of erosion of a headland.
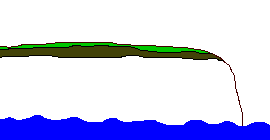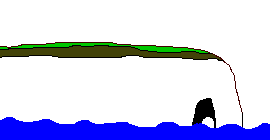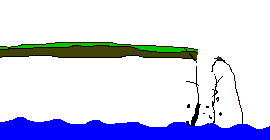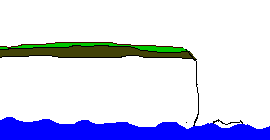
An animation showing the erosion of a headland
Stage 1 in the formation of a headland

Waves attack a weakness in the headland. The video below shows cracks in the chalk cliffs at Flamborough.
Stage 2 in the formation of a headland

A cave is formed.
Stage 3 in the formation of a headland

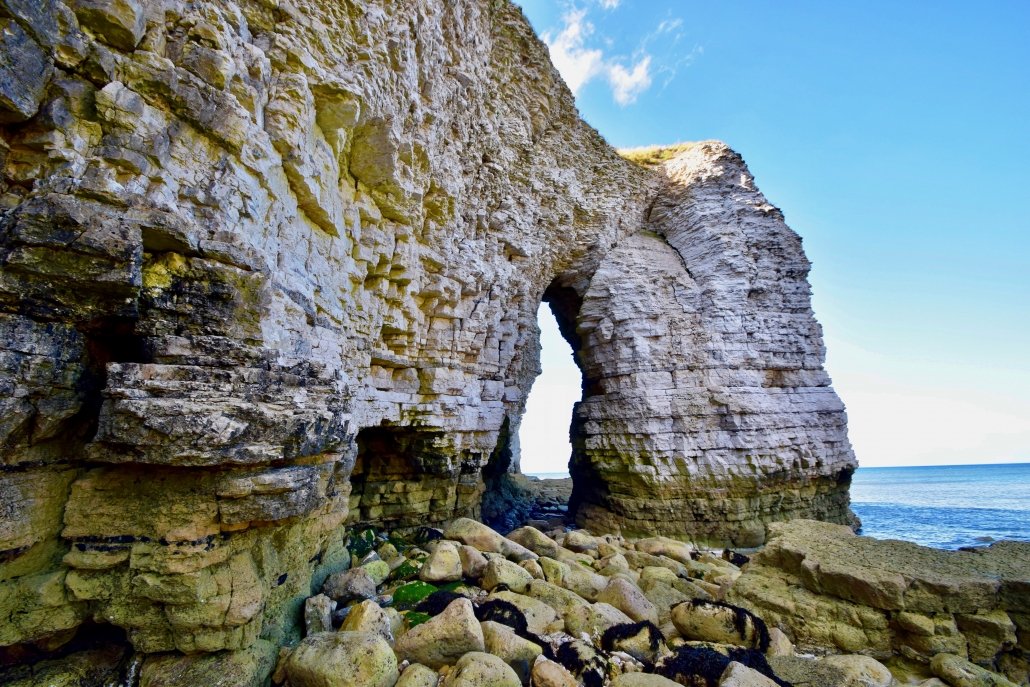
Eventually, the cave erodes through the headland to form an arch.
The image below shows an arch at Flamborough.
The most famous arch in the UK is Durdle Door, located on Dorset’s Jurassic Coast.
The video below shows an arch at Flamborough.
Stage 4 in the formation of a headland

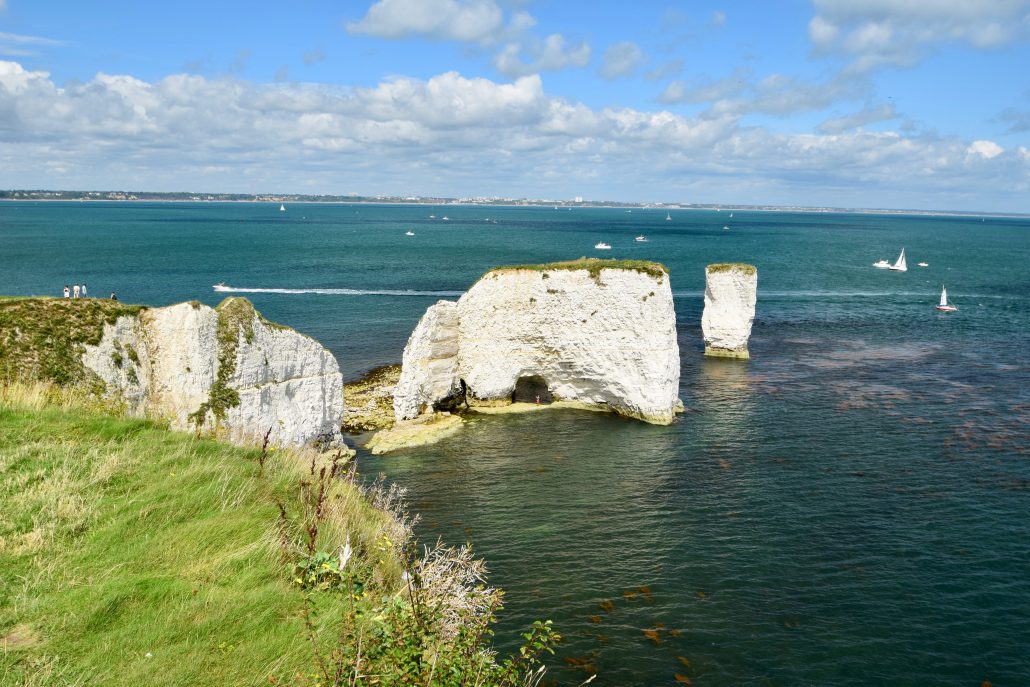
The roof of the arch collapses leaving a column of rock called a stack.
The video below shows a stack at Flamborough.
The image below shows Old Harry, a stack on the Dorset Coast. You can view more images of this stack in the Old Harry gallery.
Stage 5 in the formation of a headland
The base of the stack is then eroded, which causes it to collapse, leaving a stump.

The erosion of a headland is explored in more detail below.