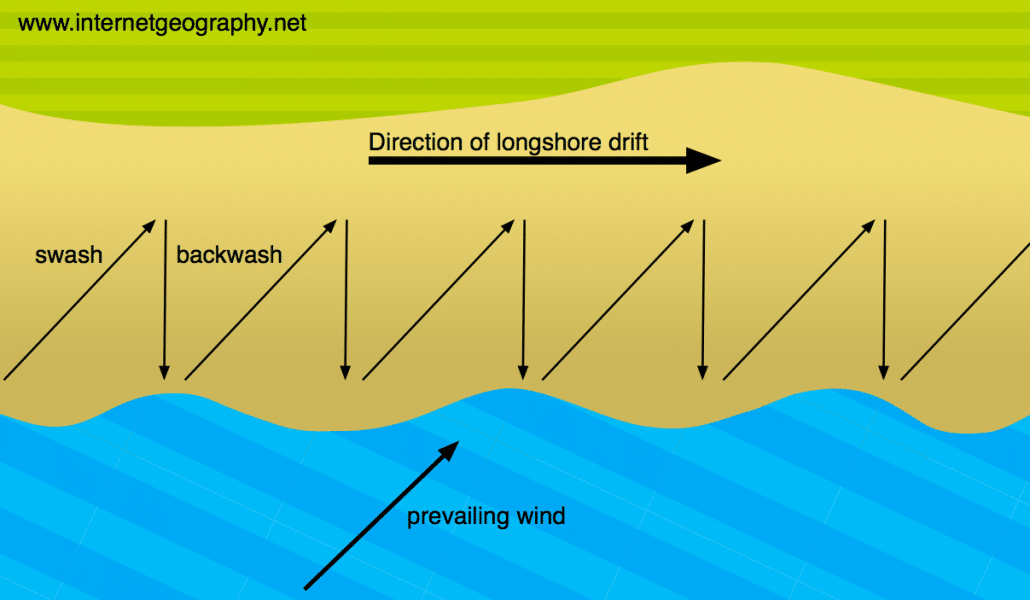
What is longshore drift?
Longshore (littoral) drift is the movement of material along the shore by wave action. It happens when waves approach the beach at an angle. The swash (waves moving up the beach) carries material up and along the beach. The backwash (waves moving back down the beach) carries material back down the beach at right angles. This is the result of gravity. This process slowly moves material along the beach and provides a link between erosion and deposition.
The material is transported through suspension, traction, solution and saltation. Longshore drift provides a link between erosion, transportation and deposition.
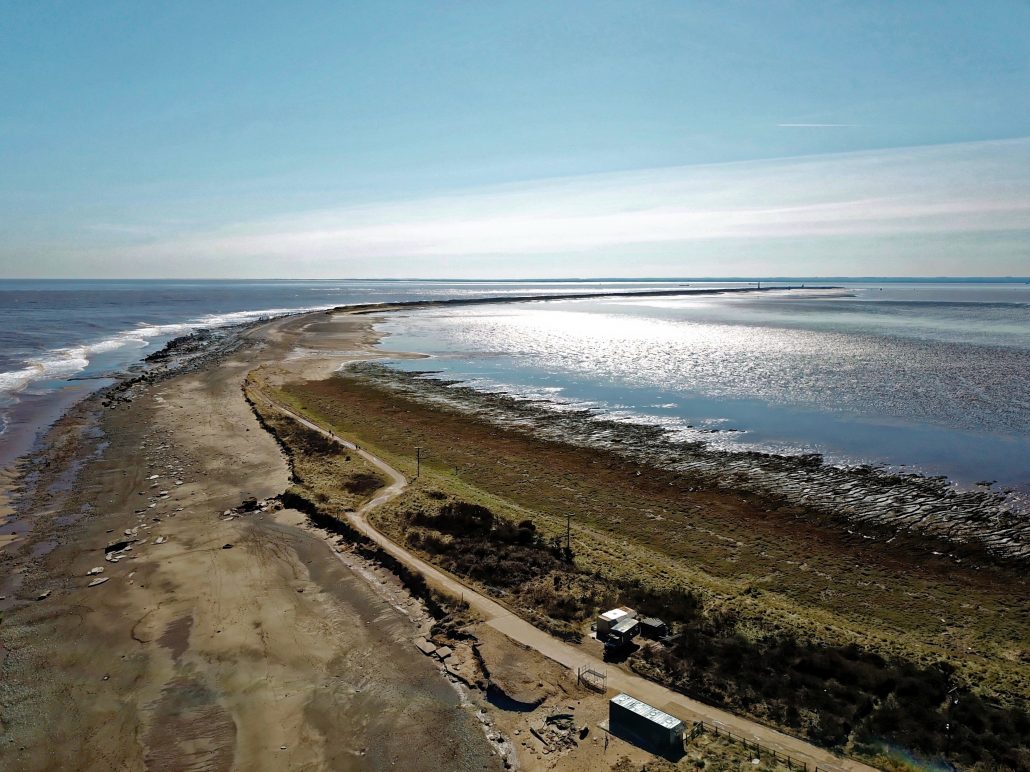
Longshore drift contributes towards the formation of a range of depositional landforms such as spits and onshore bars. For example, spurn Point is a coastal spit formed by the transportation of coastal sediment by longshore drift along the Holderness Coast. This material is then deposited at the mouth of the Humber Estuary.