What are waves?
Waves are a disturbance on the surface of the sea or ocean in the form of a moving ridge or swell.
What causes waves?
Waves are caused by energy transfer from the wind to the sea (not to be confused with tides that the Moon causes). As the wind blows over the surface of the sea, it creates friction forming waves. In deep water, water molecules within a wave move in a circular movement. It is only in shallow areas that the water itself moves forward, which occurs along the coastline where the land meets the sea.
Why are some waves stronger than others?
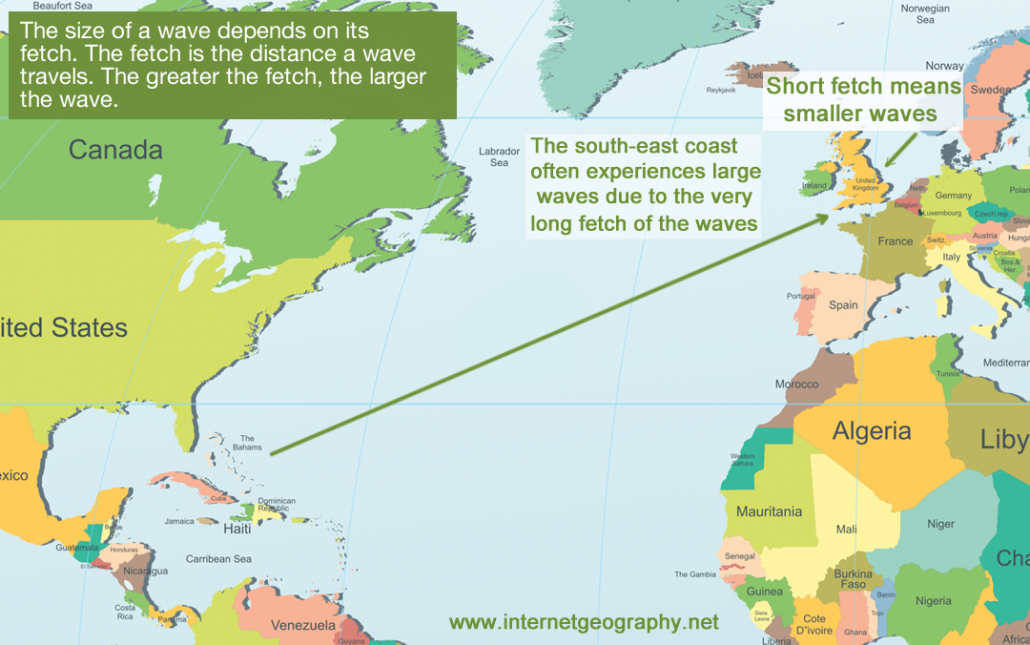
The size of a wave depends on its fetch. The fetch of a wave is the distance it travels. The greater the fetch, the larger the wave.
Wind speed also has a significant effect on the size of waves. The stronger the wind, the larger the wave because of the energy transfer. Finally, wind duration also affects the size of a wave. The longer the wind blows over the sea or ocean, the larger the wave.
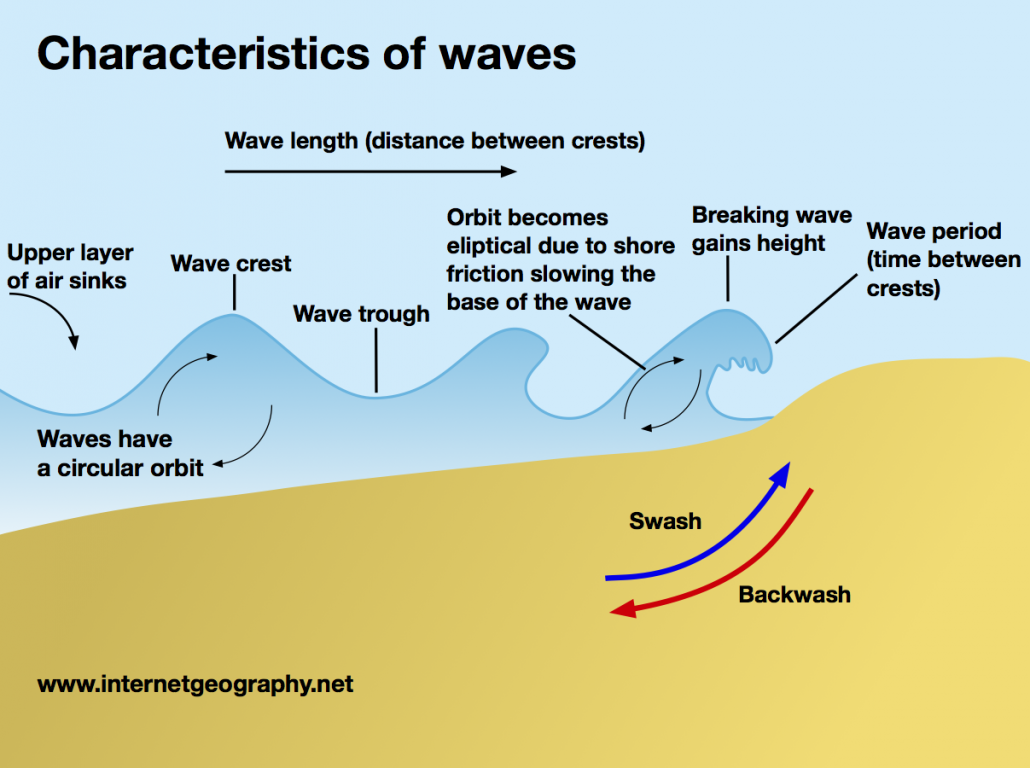
Characteristics of a wave
As waves move into shallow water, they begin to stack up as frictional drag with the seabed increases, the base of the wave is slowed down, so the top part is travelling faster, causing the wave to tilt, break and move towards the shore in the surf zone, as illustrated in the image above.
Waves can be constructive or destructive.
Summary
Flashcards
Quiz
The size of a wave depends on its fetch, wind speed and wind duration above the water. True or false?
 Internet Geography
Internet GeographyThe size of a wave depends on its fetch, wind speed and wind duration above the water.
Waves are a disturbance on the surface of the sea or ocean, in the form of a moving ridge or swell. True or false?

Waves are a disturbance on the surface of the sea or ocean, in the form of a moving ridge or swell.
What is the fetch of a wave?
 Internet Geography
Internet GeographyThe fetch of a wave is the distance it has travelled.
True or false? As waves move into shallow water, they begin to stack up as frictional drag with the seabed increases, the base of the wave is slowed down, so the top part is travelling faster. This causes the wave to tilt, break and move towards the shore in the surf zone
 Internet Geography
Internet GeographyThe movement of a wave up a beach is known as what?
 Internet Geography
Internet GeographyThe movement of water up a beach is known as swash.
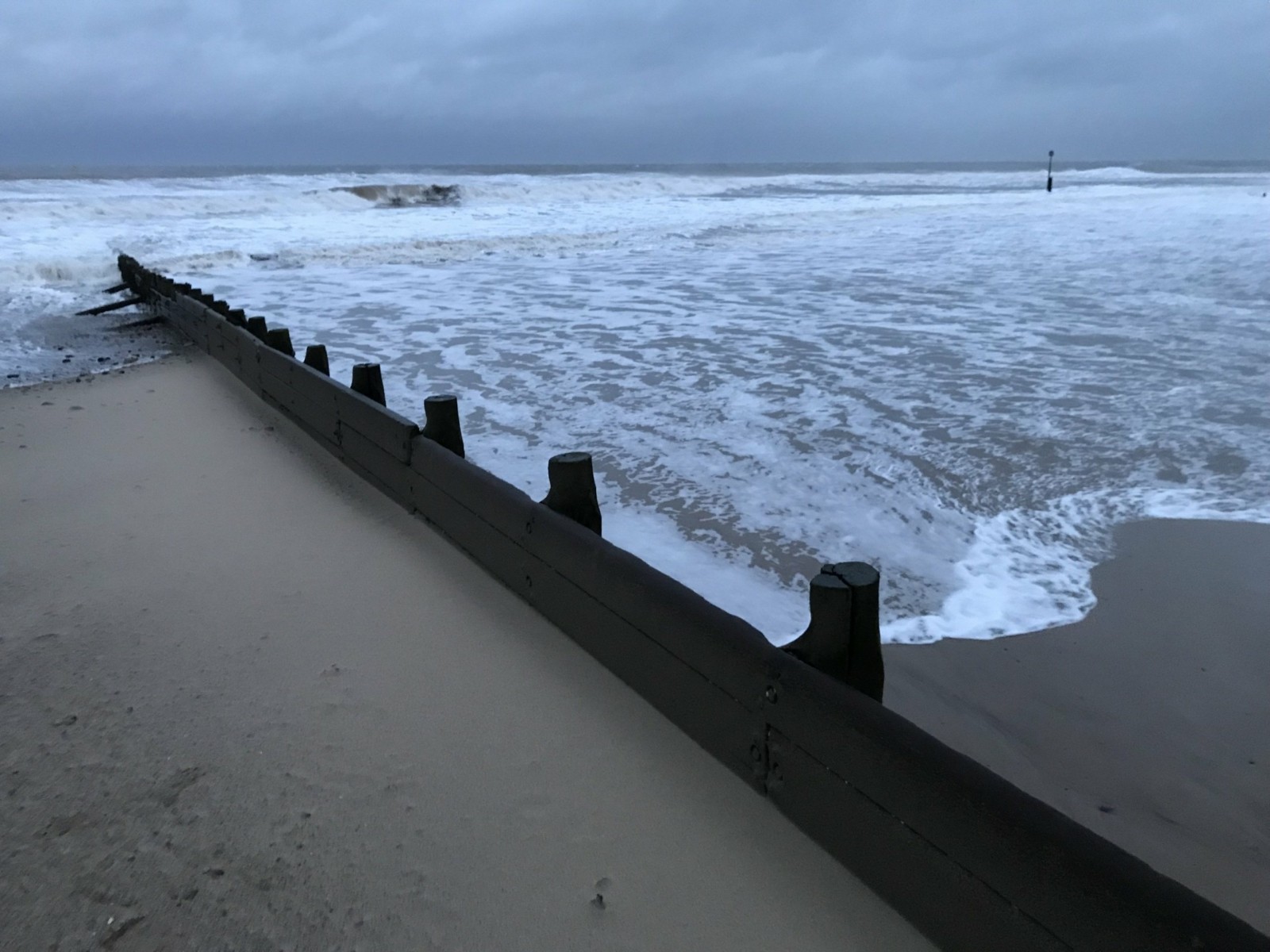
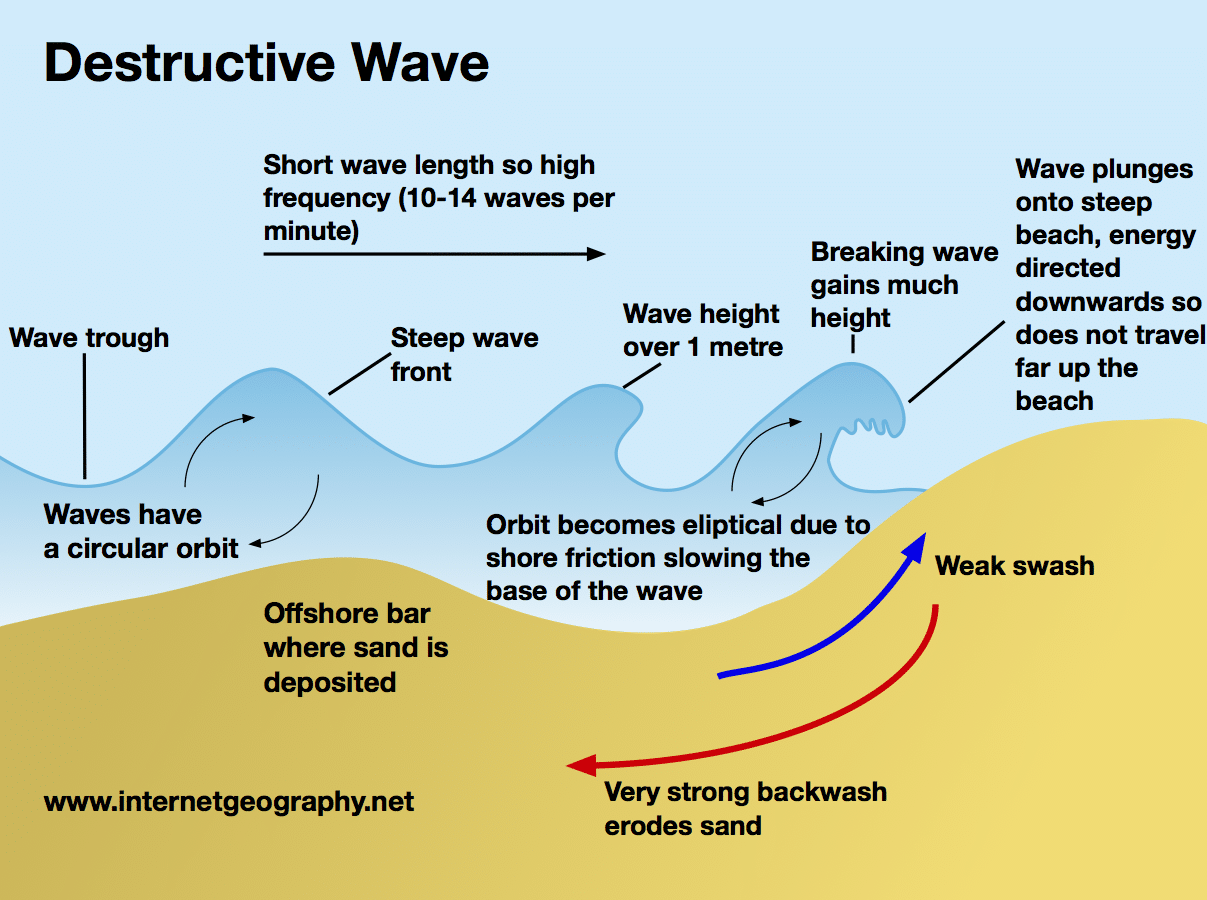
Identify the type of wave is shown in the image above.

The image shows a destructive wave. Destructive waves destroy beaches. The waves are usually very high, have a short wavelength and are very frequent. The wave has a steep front and is typically over 1 metre high. The backwash has less time to soak into the sand. As waves continue to hit the beach there is more running water to transport the material out to sea.
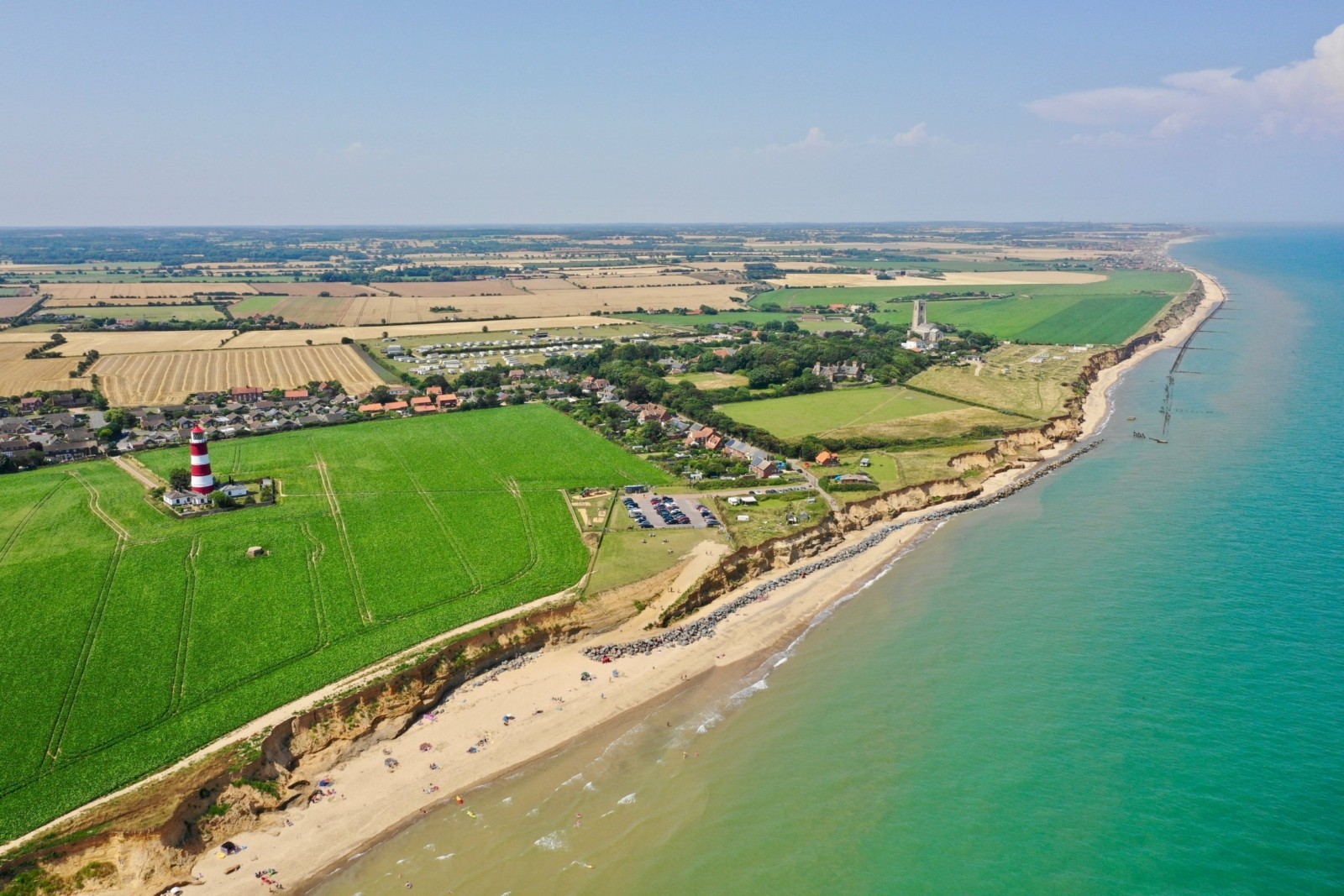
Identify the type of wave is shown in the image above.

The image shows a constructive wave. Constructive waves have a long wavelength and a low-frequency (8–10 waves per minute). They have a low wave height (typically under 1 metre). The wavefront is gently sloping and gains a little height, breaks and spills onto the beach. Water spreads a long way up the gently sloping beach.
Which of the following are characteristics of constructive waves?
 Internet Geography
Internet GeographyWhich of the following are characteristics of destructive waves?
 Internet Geography
Internet GeographyWhen are destructive waves most common?
 Internet Geography
Internet GeographyDestructive waves are more common in winter when the wind is stronger.



Share your Results: