Landforms of Coastal Erosion
Headlands and Bays
What Are They?
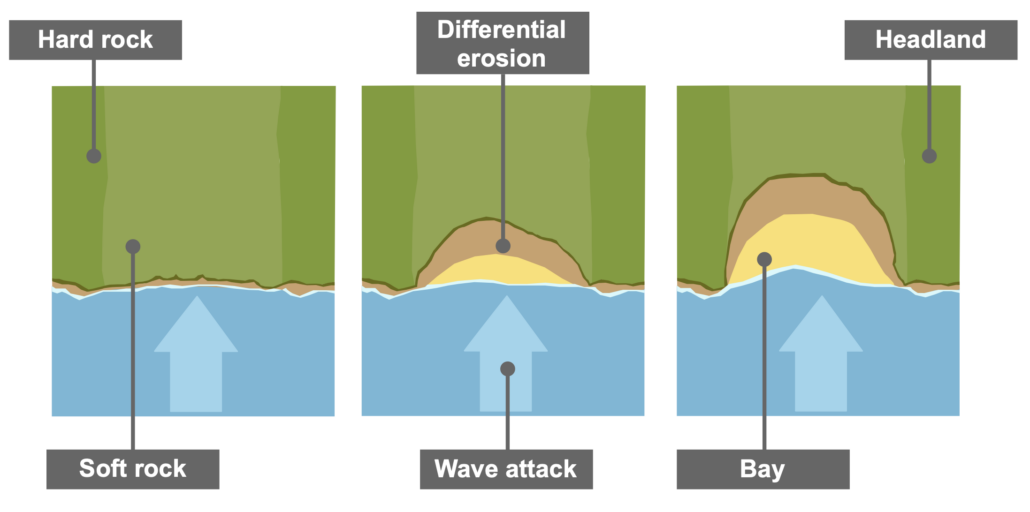
Headlands and bays are features of a discordant coastline, where bands of hard and soft rock run perpendicular to the shore. Headlands are areas of resistant rock that protrude into the sea, while bays are recesses in the coastline formed in softer, more easily eroded rock.
Characteristics
- Headlands: Steep, rocky cliffs that extend into the sea.
- Bays: Sheltered, often sandy areas between headlands, where erosion is more rapid.
Formation Process
- Differential Erosion: Softer rock (e.g., clay) erodes more quickly than harder rock (e.g., chalk or limestone).
- Headland Formation: Harder rock remains as prominent areas called headlands.
- Bay Formation: The softer rock is eroded more deeply, creating bays that are often sheltered from wave action by the adjacent headlands.
Cliffs
What Are They?
Cliffs are steep rock faces along the coast, formed as waves continuously attack the base of the rock, causing it to collapse and retreat inland over time.
Characteristics
- High, steep rock faces with a vertical drop to the shore below.
- Often found along hard rock coastlines.
Formation Process
- Wave Erosion: Waves erode the base of the cliff through processes like hydraulic action and abrasion.
- Undercutting: This creates a notch at the base of the cliff, weakening its structure.
- Collapse: The cliff above becomes unsupported and eventually collapses.
- Cliff Retreat: Over time, repeated erosion and collapse cause the cliff to retreat inland.
Wave-Cut Platforms
What Are They?
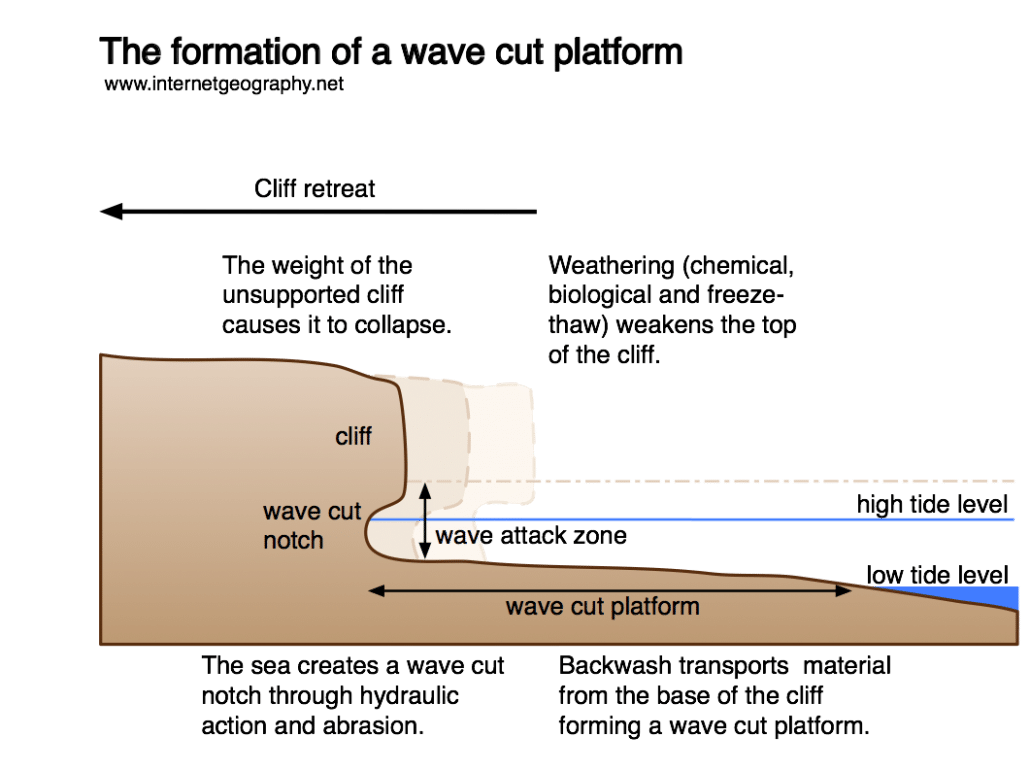
A wave-cut platform is a flat, rocky area found at the base of a retreating cliff, left behind as the cliff erodes and retreats.
Characteristics
- A flat, often smooth surface exposed at low tide.
- Found in front of retreating cliffs, extending out to sea.
Formation Process
- Undercutting: Waves erode the base of the cliff, forming a notch.
- Cliff Collapse: The cliff collapses, and the debris is carried away by wave action.
- Platform Creation: As the cliff continues to retreat, the erosion leaves behind a flat platform at the base, exposed at low tide but covered during high tide.
Caves, Arches, Stacks and Stumps
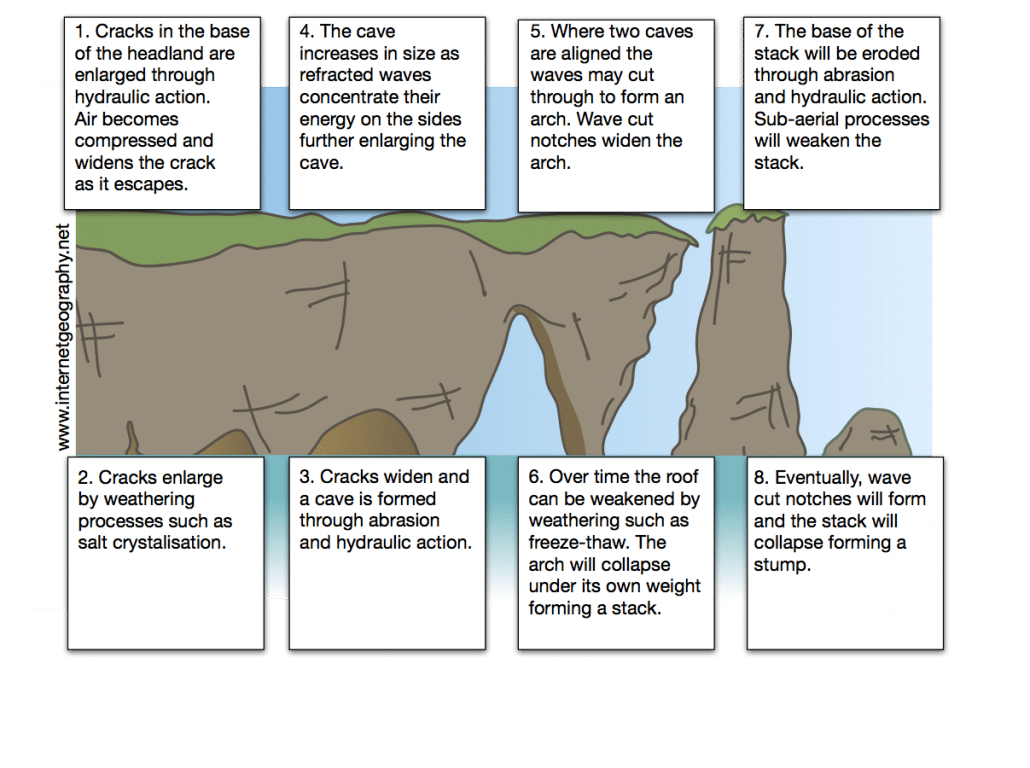
These features often form along headlands. Continuous erosion by waves on a headland can create a cave. When a cave is eroded through a headland, an arch is formed. Over time, the top of the arch can collapse due to erosion and gravity, leaving a column of rock called a stack. Further erosion at the base can cause a stack to collapse, leaving a stump. This sequential process illustrates the power of erosional forces along the coast.
These landforms are part of a continuous sequence of erosion on headlands, resulting in striking coastal features.
Caves
What Are They?
Caves are hollowed-out areas at the base of a cliff, often formed in areas of weaker rock or along joints and faults.
Characteristics
- Found at the base of headlands.
- Formed by hydraulic action and abrasion.
Formation Process
- Crack Formation: Hydraulic action forces water into cracks in the cliff.
- Widening Cracks: Abrasion and hydraulic action widen the cracks, eventually forming a cave.
Arches
What Are They?
An arch is a curved rock formation where a cave has broken through a headland, creating an opening from one side to the other.
Characteristics
- A natural arch-shaped opening in a headland.
- Usually found along hard rock coasts.
Formation Process
- Cave Enlargement: Erosion continues to enlarge a cave, deepening it.
- Arch Formation: The cave eventually breaks through the other side of the headland, forming an arch.
Stacks
What Are They?
Stacks are tall, isolated pillars of rock left standing in the sea after the collapse of an arch.
Characteristics
- Isolated columns of rock, usually close to the shoreline.
- Formed from resistant rock, standing after the collapse of an arch.
Formation Process
- Arch Collapse: The roof of the arch becomes too weak to support itself and collapses due to further erosion and weathering.
- Stack Creation: The isolated column of rock left behind is called a stack.
Stumps
What Are They?
Stumps are shorter, eroded remnants of stacks that have been worn down by wave action.
Characteristics
- Shorter and often submerged at high tide.
- Found at the base of where a stack once stood.
Formation Process
- Stack Erosion: Continuous erosion weakens the base of the stack.
- Stack Collapse: The stack collapses, leaving behind a smaller stump that is further eroded by waves.