Landforms of Coastal Deposition Flashcards
A sandy beach is usually formed in a sheltered bays, where low energy, constructive waves transport material onto the shore.
Find out more about landforms of coastal deposition.
Beaches, sand dunes, spits and bars.
Find out more about landforms of coastal deposition.
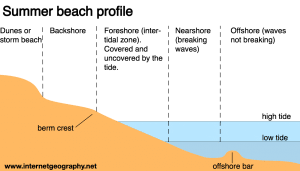
Offshore bars form when sediment is transported on and off a beach. Destructive waves remove sediment from the beach and form the offshore bar.
Find out more about landforms of coastal deposition.
A bar is created when there is a gap in the coastland with water in it. This could be a bay or a natural hollow in the coastland. The process of longshore drift occurs and this carries material across the front of the bay. Material is pushed up onto beaches at a 45-degree angle when the swash brings it onto the coastline. The backwash takes it back out towards the sea at a right angle to the coast. Through this process, the material is constantly moved along the coastline. The deposited material eventually joins up with the other side of the bay and a strip of deposited material blocks off the water in the bay. The area behind the newly formed bar is known as a lagoon.
Find out more about landforms of coastal deposition.