Landforms of Coastal Erosion Flashcards
What is a bay?
Click to View the Answer
Click to View the Question
A bay is an inlet of the sea where the land curves inwards.
Find out more about bays.
What is a bay?
What is a headland?
Click to View the Answer
Click to View the Question
A headland is a cliff that sticks out into the sea and is surrounded by water on three sides.
Find out more about headlands.
What is a headland?
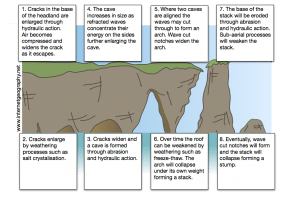
Produce an annotated diagram to show the formation of a stump.
Click to View the Answer
Click to View the Question
Find out more about the erosion of a headland.
Produce an annotated diagram to show the formation of a stump.
What is a wave-cut platform?
Click to View the Answer
Click to View the Question
A wave-cut platform is a wide, gently sloping surface found at the base of the cliff and extends into the sea.
Find out more about wave-cut platforms.
What is a wave-cut platform?
Identify your case study location for landforms of coastal erosion.
Click to View the Answer
Click to View the Question
The case study location will be identified e.g. Flamborough Head / Durdle Door / Old Harry Rocks.
Identify your case study location for landforms of coastal erosion.