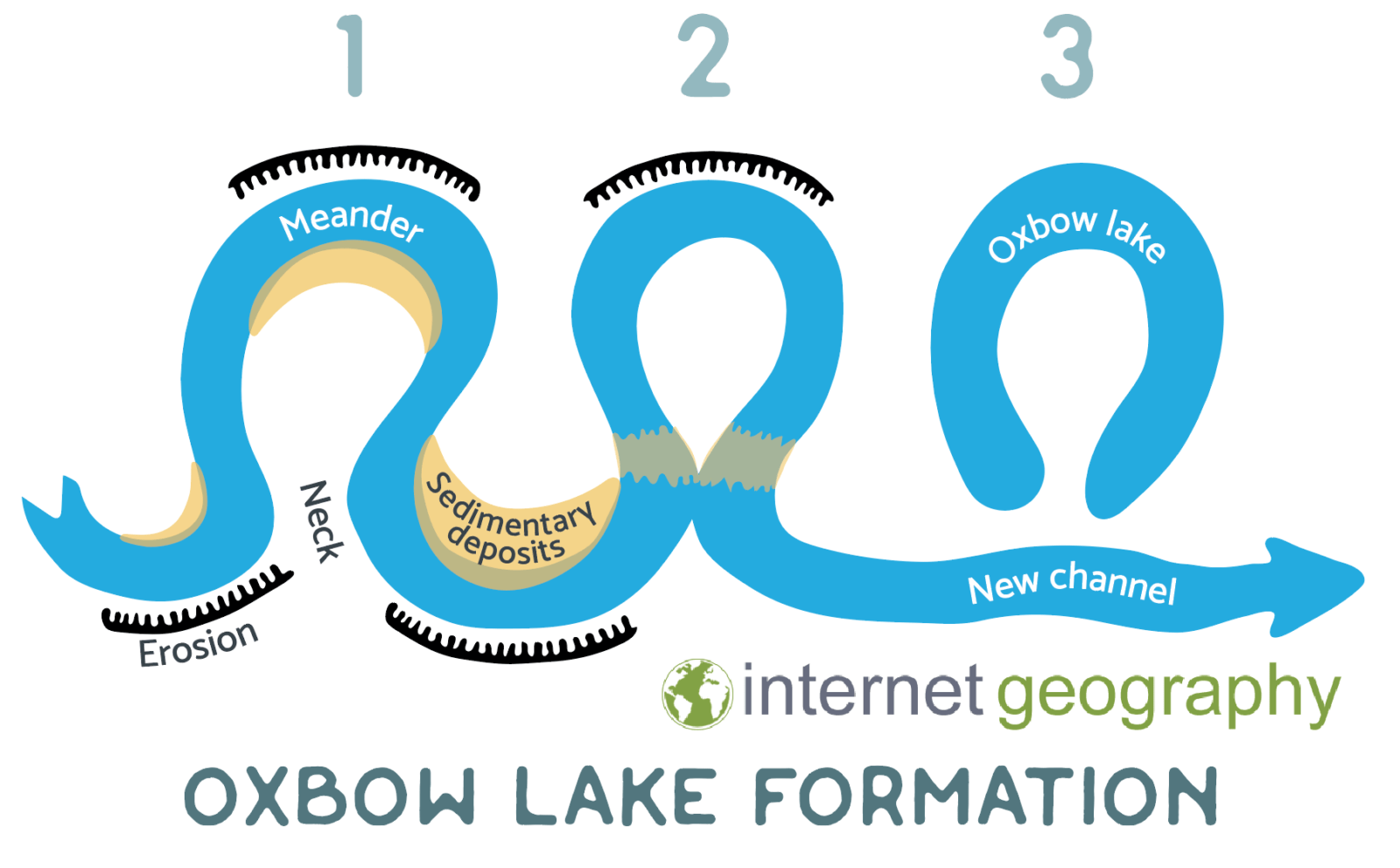Rivers Flashcards
Economic benefits of constructing dams and reservoirs include:
- boosting tourism e.g. the local economy of Kielder has been boosted by £6 million thanks to the construction of Kielder Dam
- they can be used to produce electricity by passing the water through a turbine within the dam
Find out more about hard engineering.
When a river floods friction with the floodplain leads to a rapid decrease in the velocity of the river and therefore its capacity to transport material. Larger material is deposited closest to the river bank. This often leads to large, raised mounds being formed. Smaller material is deposited further away and leads to the formation of gently sloping sides of the levees.
Find out more about landforms in the lower course of the river.
It becomes narrow and steep-sided in the upper course due to vertical erosion.
Find out more about the long profile of a river.
The characteristics of rapids include:
- the turbulent flow of water
- white water
- uneven river bed
- steep gradients.
Find out more about the landforms of erosion in the upper course of a river.
Find out more about meanders and oxbow lakes.