Coastal Landscapes in the UK Flashcards
What is coastal erosion?
Click to View the Answer
Click to View the Question
Coastal erosion is the wearing away of the land by the sea.
Find out more about the processes of coastal erosion.
What is coastal erosion?
What is soft engineering?
Click to View the Answer
Click to View the Question
Soft engineering does not involve building artificial structures but takes a more sustainable and natural approach to manage the coast.
Find out more about soft engineering techniques.
What is soft engineering?
Describe the characteristics of rock that has recently gone through freeze-thaw.
Click to View the Answer
Click to View the Question
Recently weathered rock can be seen at the foot of chalk and limestone cliffs and is easily identified because it is angular.
Find out more about weathering.
Describe the characteristics of rock that has recently gone through freeze-thaw.
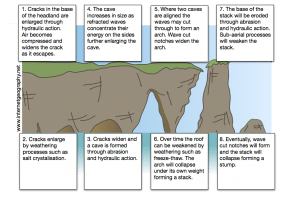
Produce an annotated diagram to show the formation of a stump.
Click to View the Answer
Click to View the Question
Find out more about the erosion of a headland.
Produce an annotated diagram to show the formation of a stump.
Give three examples of hard engineering techniques used to protect the coast.
Click to View the Answer
Click to View the Question
Groynes, rock armour, sea walls, revetments, gabions or breakwater.
Find out more about hard engineering at the coast.
Give three examples of hard engineering techniques used to protect the coast.