Why is there uncertainty about global temperature change projections?
A central concern with global warming is the unpredictability of future climate changes. Predictions for global sea level rise by 2100 vary from 20 cm to over 100 cm. The accompanying graph indicates that by 2100, the global average temperature might increase by 1 to 5 °C compared to present levels.
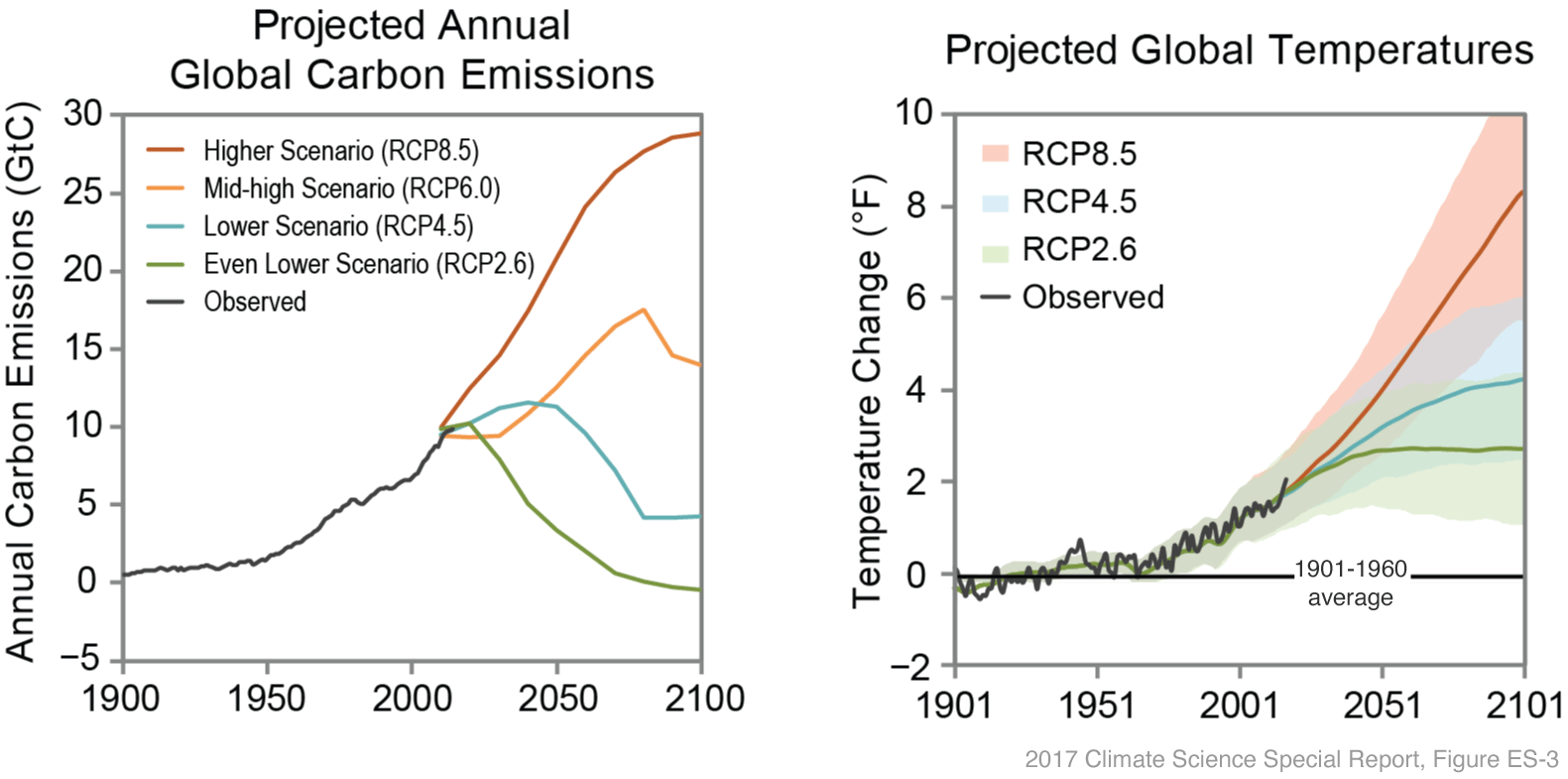
Projected carbon emissions vs projected average global temperature – Source: https://www.climate.gov/media/12886
This uncertainty arises from both human activities and natural processes. These factors are linked to the potential magnitude of future greenhouse gas emissions and how Earth’s climate system might respond to increased emissions in the future.
What are the human factors contributing to this uncertainty?
- The future global population is uncertain. By 2100, it could range between 9 billion and 13 billion.
- Emissions per person are tied to wealth, but predicting future average wealth is challenging.
- There is uncertainty about whether humans will significantly reduce emissions or continue to pollute at current rates.
- New technologies might emerge to replace fossil fuels, potentially lowering emissions.
What are the natural processes that contribute to uncertainty?
- The oceans’ capacity to absorb CO2 might reach a limit, affecting their ability to mitigate CO2 levels.
- As Arctic sea ice and snow cover diminish, more solar radiation gets absorbed rather than reflected, causing accelerated warming.
- The ice sheets in Greenland and Antarctica could melt faster in the future, significantly raising global sea levels.
- A warmer Earth might lead to increased cloud cover; these clouds could reflect more solar radiation back into space, potentially offsetting some warming.
Related Topics
Use the images below to explore related GeoTopics.


