Global patterns of water surplus and deficit
What are global patterns of water surplus and deficit?
Water security/insecurity
Water security refers to the availability of adequate, clean water to support health, well-being, and economic growth. When regions lack enough safe water, they face water insecurity or water scarcity. This can result from physical factors affecting supply, such as insufficient rainfall or saltwater intrusion into underground reservoirs (aquifers). Human factors like over-extraction from aquifers and population growth also affect water insecurity. The map below illustrates global patterns of water scarcity.
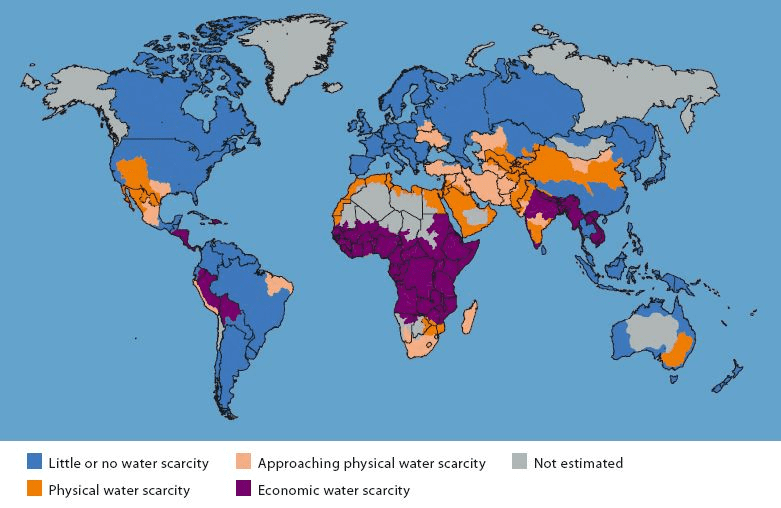
Water Scarcity – Source
- Physical scarcity: Occurs in areas with low rainfall, such as arid and semi-arid regions.
- Economic scarcity: Found in regions with water resources but lacking the infrastructure to utilise them effectively.
Water scarcity affects every continent except Antarctica, with Africa experiencing the most severe and widespread conditions. The UN estimates that approximately 1.2 billion people suffer from physical water scarcity, while another 1.5 billion experience economic scarcity.
Global patterns of water surplus and deficit
Global patterns of water surplus and deficit are shown in the map below. Regions with a water surplus, where supply exceeds demand, include North America, Europe, and parts of Asia. Conversely, areas with a water deficit, where demand exceeds supply, are under pressure.
Regions with high rainfall typically enjoy a water surplus, while areas with low rainfall, such as deserts, are more likely to have a water deficit. High population density and industrial activity increase water demand, potentially leading to water deficits if the supply is inadequate. Conversely, areas with low rainfall and low demand might still maintain a water surplus.
What is Water Stress?
Many countries experience high water stress. High water stress occurs when more than 80% of available water is used annually, posing a risk of water scarcity. A country begins to face water stress when the per capita water availability falls below 1700 cubic meters per year. If this availability drops below 1000 cubic meters, water stress can hinder economic development and negatively impact human health and well-being. Regions with significant water stress include several Caribbean islands, Bahrain, and Cyprus.
What are the reasons for increasing water consumption?
Global water consumption has significantly increased over the last few decades due to population growth, economic development, and agriculture.
Economic Development
As economies develop, the demand for water increases. Demand for water in HICs is considerably higher than in NEEs and LICs. However, as NEEs and LICs develop further, their water demand will also significantly increase.
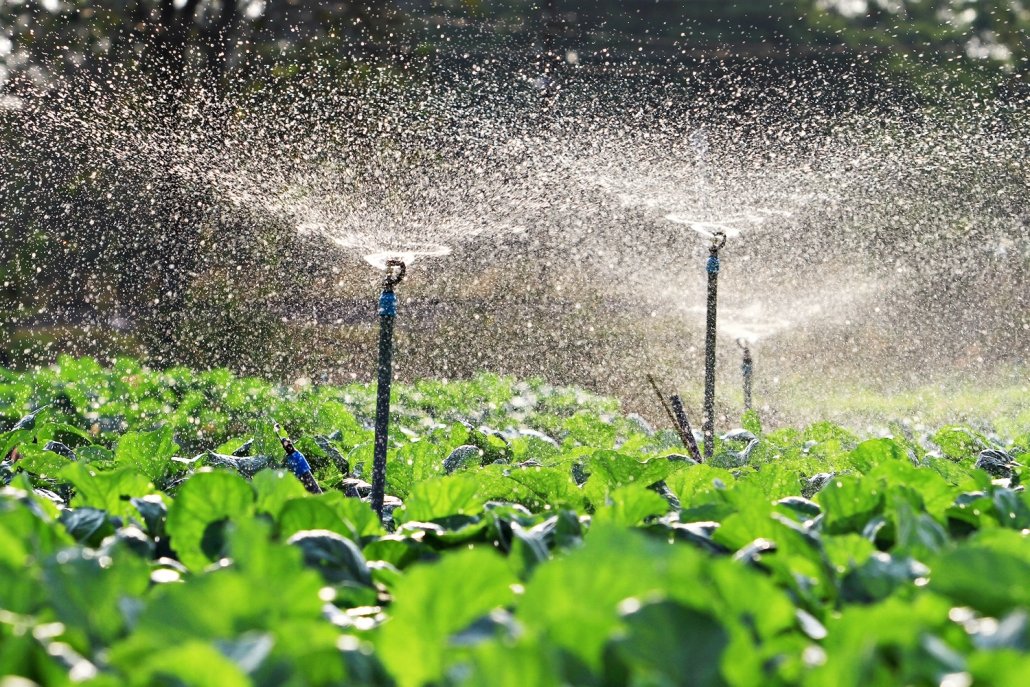
As demand for food increases, pressure is put on agricultural systems to become more intensive. This requires significantly more water for irrigation and processing. By 2050, global demand for food is expected to increase by 70 per cent.

Irrigation
Processing and manufacturing industries require considerable amounts of water. Industrial processes can lead to increased water pollution, reducing availability within a country.
The demand for water for drinking, washing and sanitation increases with urbanisation. Areas that are already experiencing water stress are those with the greatest potential for urbanisation in the future.
As people become wealthier, their water demand increases. Wealth leads to purchasing more home appliances and a greater demand for leisure activities such as golf that require water.
Population growth
Over the last 70 years, there has been considerable growth in the world’s population. Much of this growth has happened in LICs and NEEs, many of which already suffer water insecurity and water deficit. The fastest population growth is occurring on the African continent, presenting significant challenges in providing fresh water for all.
Related Topics
Use the images below to explore related GeoTopics.




