Cliffs and Wave-cut Platforms
Cliffs and wave-cut platforms are landforms formed through erosion, commonly found along the coast.
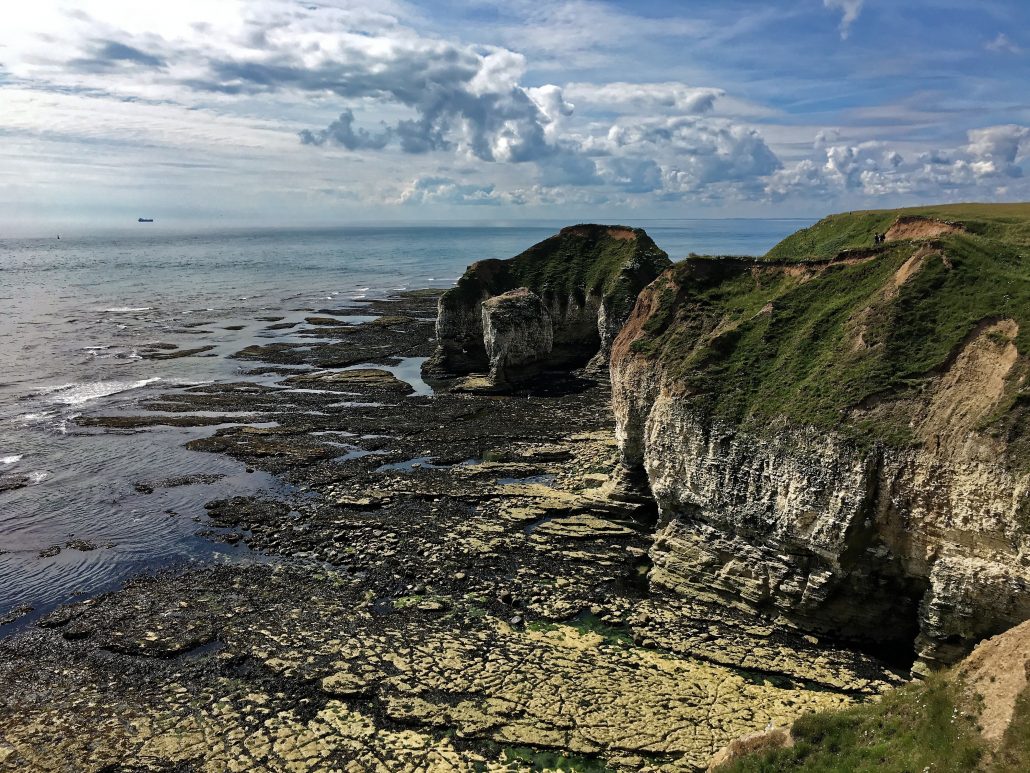
Processes of coastal erosion and weathering are responsible for shaping cliffs. Less resistant (soft) rock erodes quickly, forming gently sloping cliffs. More resistant (hard) rock forms steep cliffs.
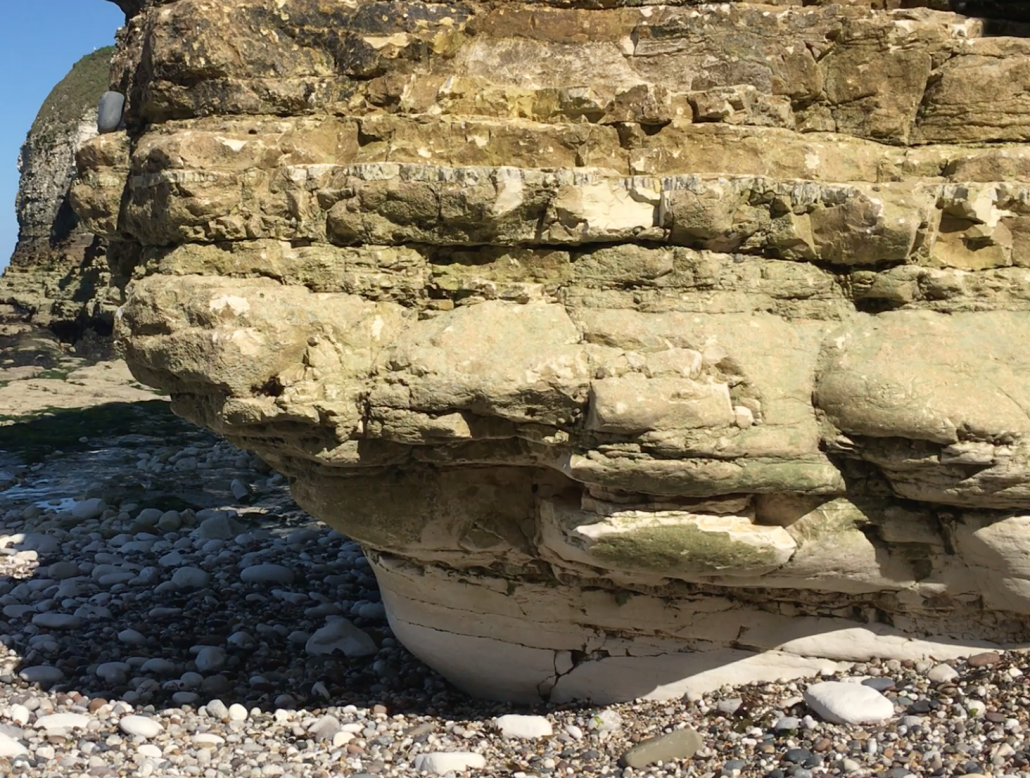
Where cliffs are made from more resistant rock, wave-cut platforms are often formed. A wave-cut platform is a wide, gently sloping surface found at the base of the cliff and extending into the sea. The image below shows a wave-cut platform formed at Flamborough, Holderness Coast.
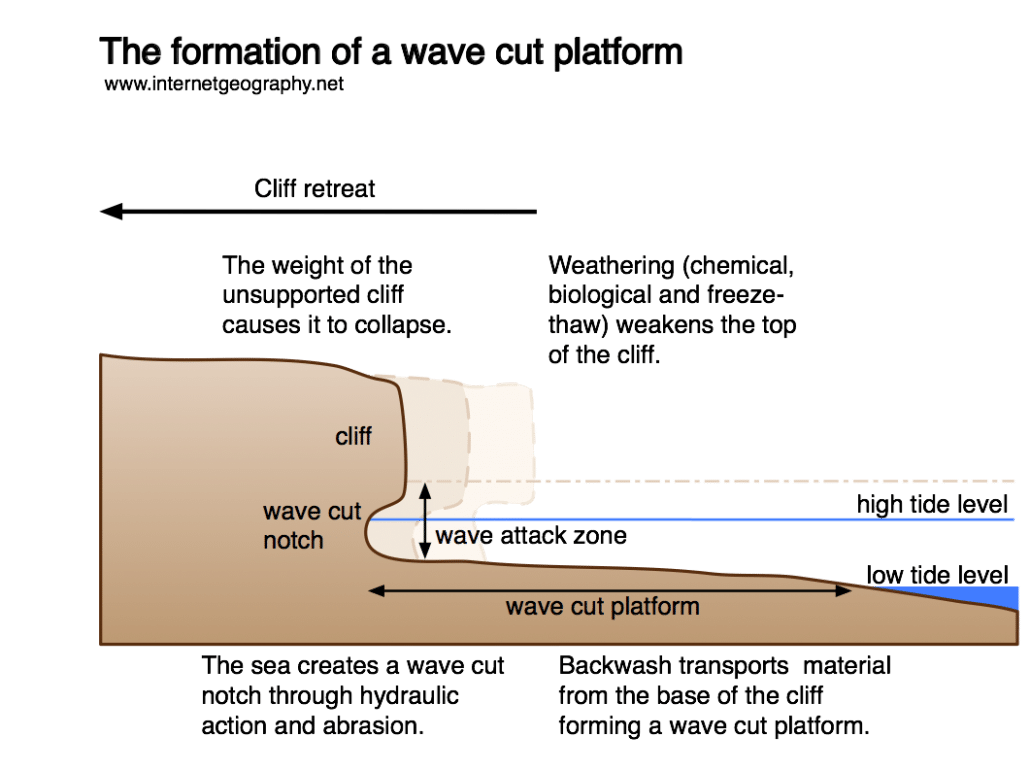
A wave-cut platform is formed when:
- The sea attacks a weakness in the base of the cliff. For example, this could be a joint in chalk.
- A wave-cut notch is formed through erosional processes, including hydraulic action and abrasion.
- As the notch becomes larger, the cliff becomes unstable and collapses due to gravity.
- The cliff retreats inland.
- The material from the collapsed cliff face is eroded and transported away. This leaves a wave-cut platform.
- The process repeats over time.