How has climate changed since the beginning of the Quaternary period?
Climate change refers to any significant change in the Earth’s climate over a long period of time. Global temperatures have fluctuated (gone up and down) throughout the Earth’s history.
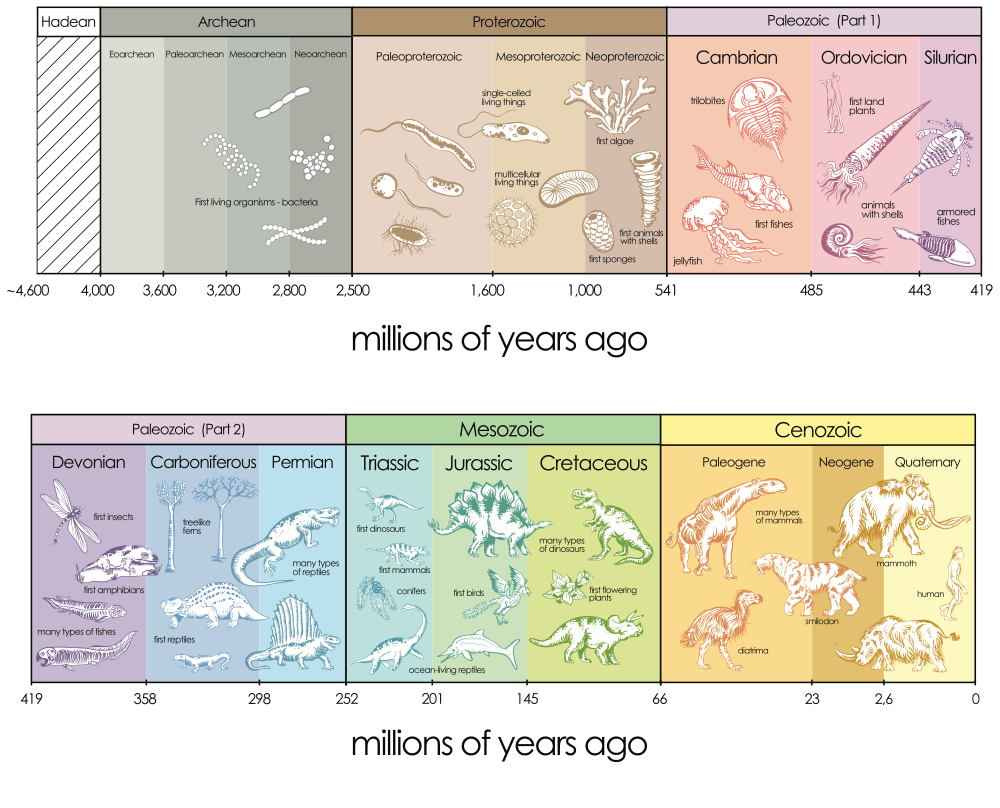
The Earth is estimated to be 4.55 billion years old, and its history has been divided into eras, periods and epochs through a geological timescale.
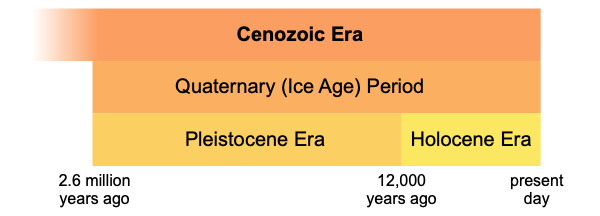
The current period, known as the Quaternary period, spans from approximately 2.6 million years ago to the present and is part of the Cenozoic era. The Quaternary period marks a cooling trend, starting the most recent ice age (out of five believed to have occurred). It is divided into two epochs: the Pleistocene and the Holocene.
The Earth’s climate was warmer and more stable before the Quaternary period. Since then, things have undergone significant changes.
Global temperatures have shifted between cold glacial periods and warmer interglacial periods. As you can see from the graph below, glacial periods have lasted around ten times longer than interglacial periods.
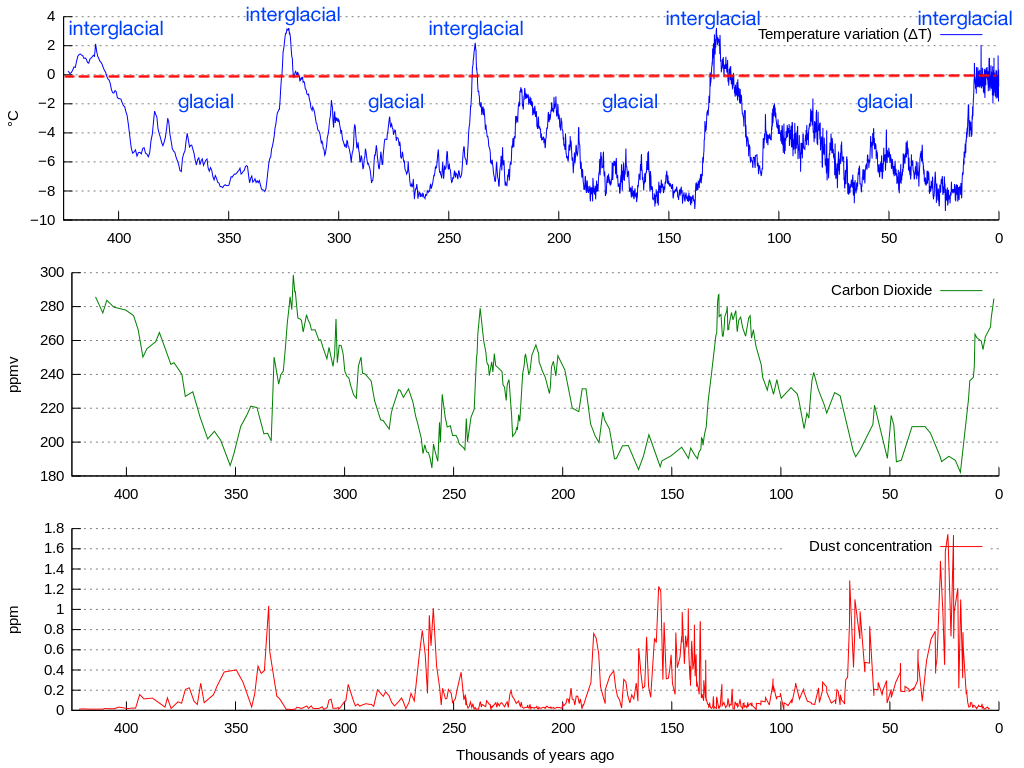
Ice core data for the past 400,000 years, with the present at right. Note the length of glacial cycles averages ~100,000 years. The blue curve is temperature, the green curve is CO2, and the red curve is windblown glacial dust (loess). Image a derivative of By Vostok-ice-core-petit.png: NOAA derivative work: Autopilot (Vostok-ice-core-petit.png) [CC-BY-SA-3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/) or GFDL (http://www.gnu.org/copyleft/fdl.html)], via Wikimedia Commons
What is the Evidence for Climate Change?
Global climate change occurs over thousands of years at a very slow pace. Since 1914, the Met Office has recorded reliable climate change data using weather stations, satellites, weather balloons, radar and ocean buoys. The Earth’s average surface temperature has increased by approximately 1 °C over the last 100 years. Additionally:
- Since 1900, sea levels have risen by 19 centimetres and are expected to rise due to thermal expansion and melting ice sheets.
- Ocean temperatures are the warmest since 1850, and glaciers are retreating.
Scientists have used a range of evidence to work out changes in the Earth’s climate.
Ice and Sediment Cores
An ice core is a sample taken from a glacier or ice sheet. It involves drilling down into the ice and removing a cylinder of ice. As ice is formed in layers, it is possible to analyse gases from each year. From this, scientists can work out the temperature at the time. Ice cores can be taken from Antarctica, providing information on the last 400,000 years. Samples of sediment taken from the ocean floor can also indicate temperature over time. It has been possible to gather data from the last 5 million years by using this technique.
Temperature Records
Thermometers have been used to measure temperature accurately since the 1850s. This provides reliable, short-term data on climate change.
Tree Rings
Each year a tree grows, it forms a new ring. The width of the ring indicates the climatic conditions for the year. The thicker the ring, the warmer and wetter the climate for that year. Tree rings help give an indication of climatic conditions over time.
Pollen Analysis
Analysing pollen preserved in peat bogs or lake sediments reveals the species that inhabited the past. This indicates temperatures based on our understanding of the conditions in which different plants thrive.