What is Continental Drift?
In 1912, Alfred Wegener published a theory to explain why the Earth looked like a huge jigsaw. He believed the continents were once joined, forming a supercontinent he called Pangaea. Over 180 million years ago, this supercontinent began to “break up” due to continental drift.
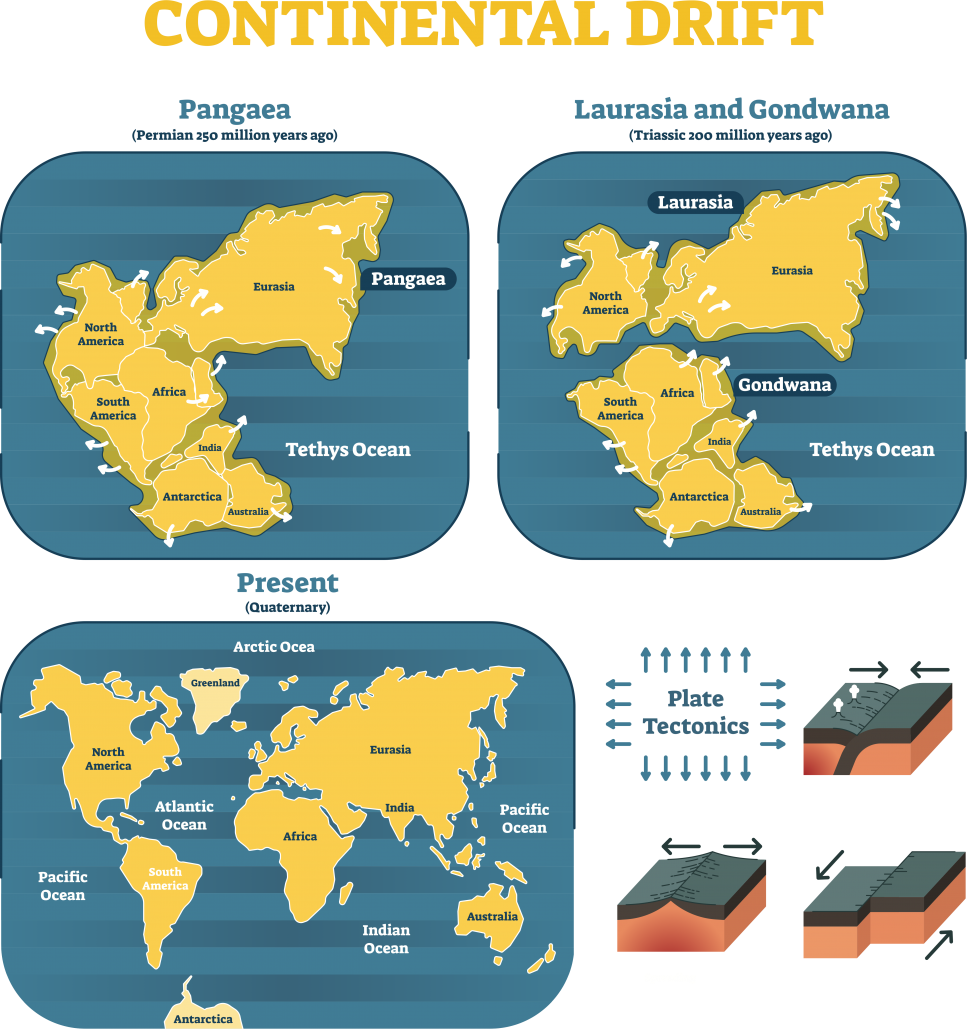
Continental drift
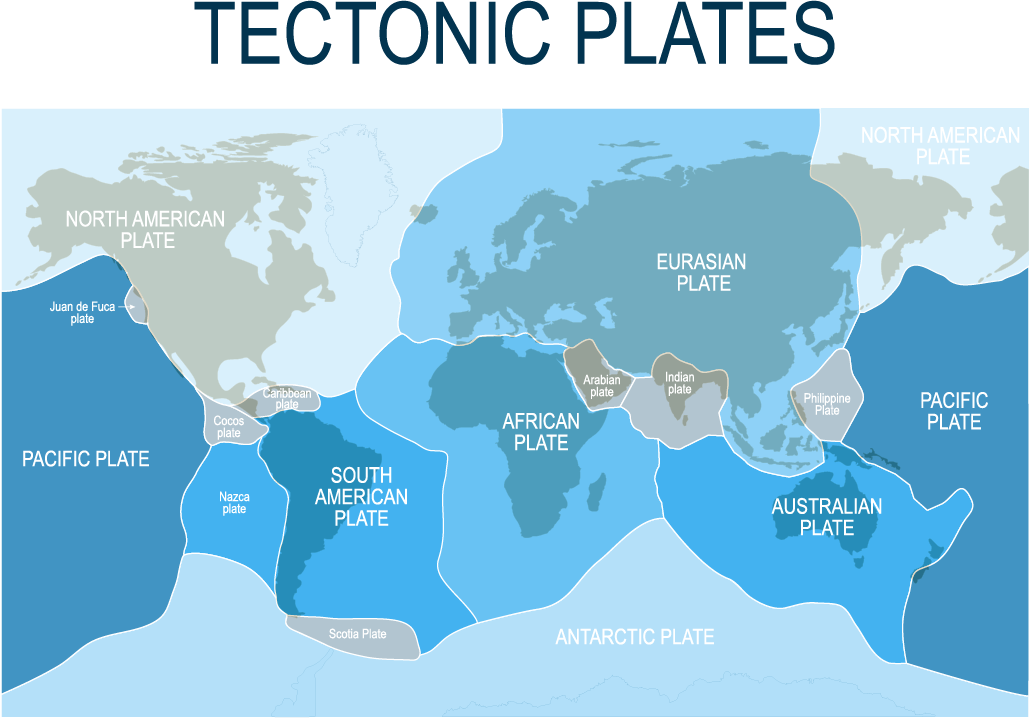
During the 20th Century, scientists developed the theory of Plate Tectonics. The theory suggests that the crust of the Earth is split up into seven large plates (see map below) and a few smaller ones, all of which can slowly move around on the Earth’s surface. They lie on the ductile mantle that allows them to move. There are several explanations for the movement of the Earth’s plates, and these are explored in the Why do plates move? page.
What is the evidence for continental drift?
Wegener’s evidence for continental drift was that:
- the same types of fossilised plants and animals are found in South America and Africa;
- the east coast of South America fits the west coast of Africa like a jigsaw puzzle;
- rock formations and mountain chains match in South America and Africa;
- similar mineral deposits and natural resources, such as coal, exist along the east coast of Africa and the west coast of South America.