What causes climate change?
The atmosphere traps some of the heat reflected from the Earth’s surface. This natural process is known as the greenhouse effect. Without this natural process, the Earth’s temperatures would be much colder. For example, without naturally occurring greenhouse gases, Earth’s average temperature would be near -18°C instead of the much warmer 15°C.
The greenhouse effect works by allowing the atmosphere to pass heat from the Sun (short-wave infrared radiation) through to warm the Earth’s surface. The surface of the heat then gives off heat as longwave radiation. Some of this heat is trapped by natural greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide, which radiate the heat back towards Earth, thereby heating the Earth.
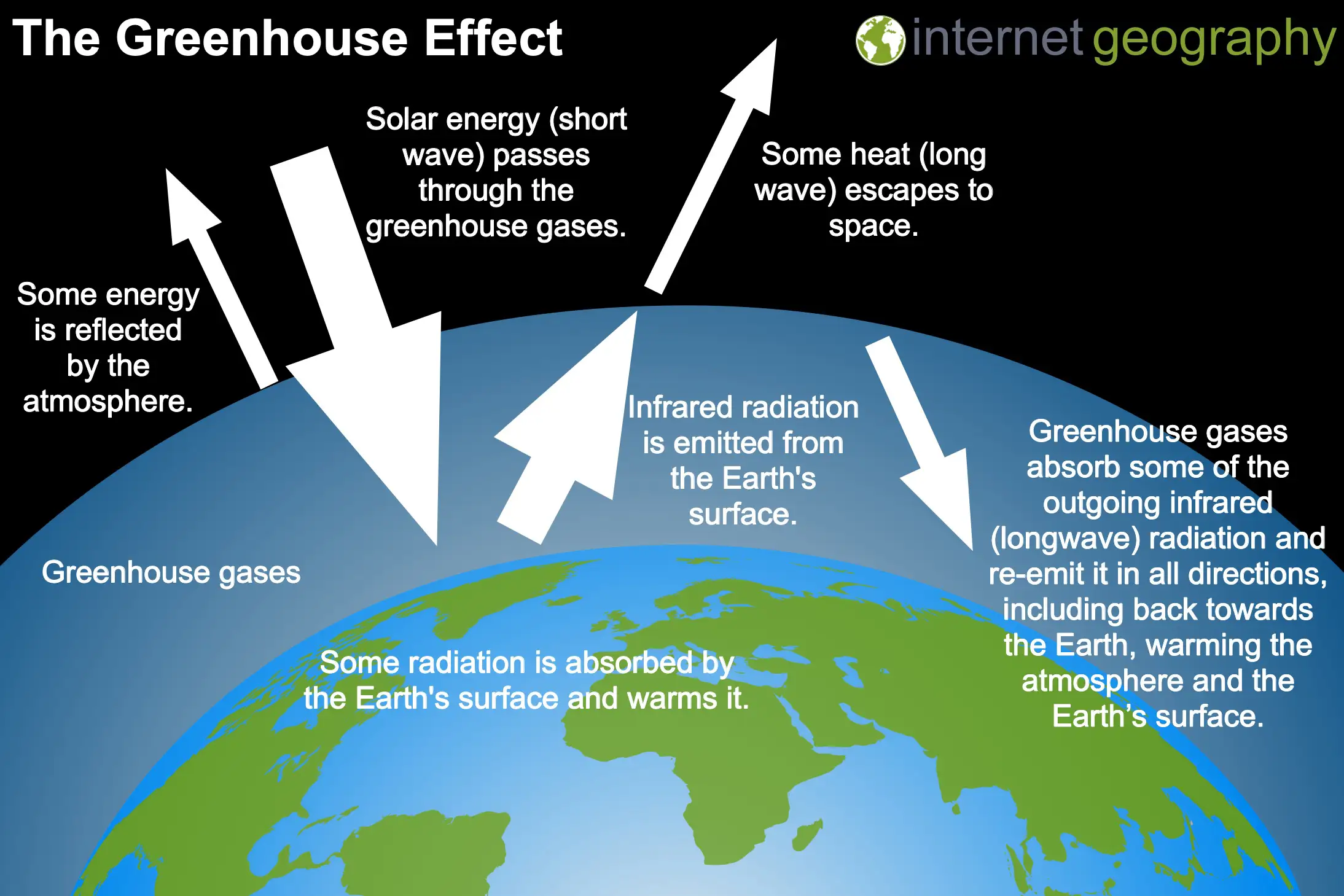
The Greenhouse Effect
Human factors enhancing the greenhouse effect
Human activities increase the volume of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, leading to the enhanced greenhouse effect, as increased greenhouse gases trap more of the infrared heat reflected by the Earth’s surface. The average global temperature increases as a result.
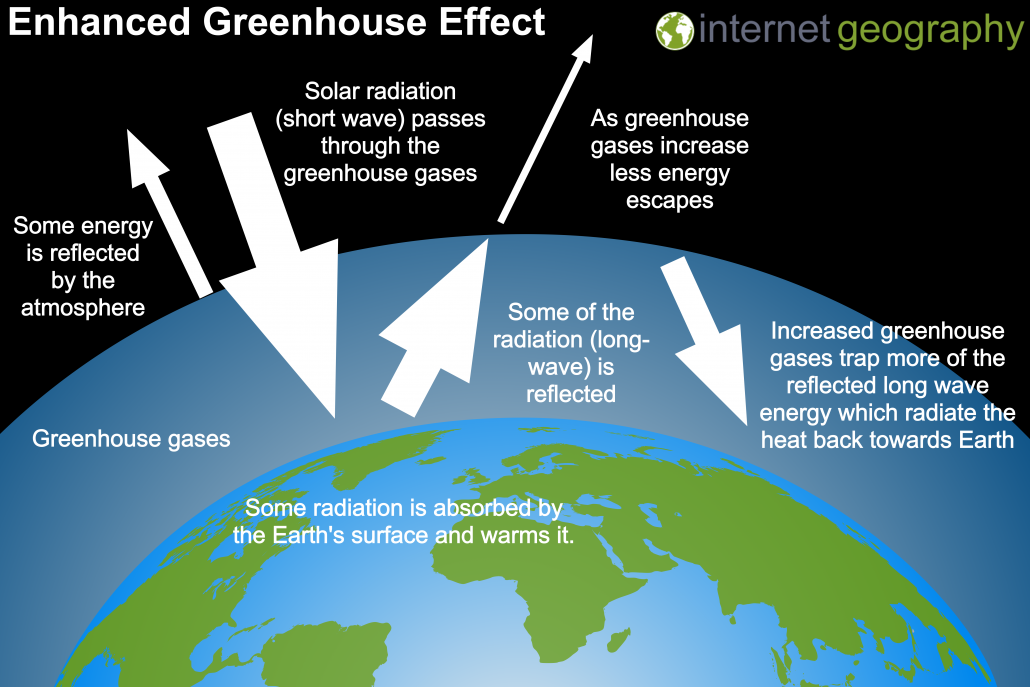
Enhanced Greenhouse Effect
Human activities that lead to an increase in greenhouse gases in the atmosphere include:
- Deforestation (cutting down trees) – Trees absorb carbon dioxide during photosynthesis. When trees are cut down, less carbon dioxide will be absorbed, leading to increased concentrations in the atmosphere.
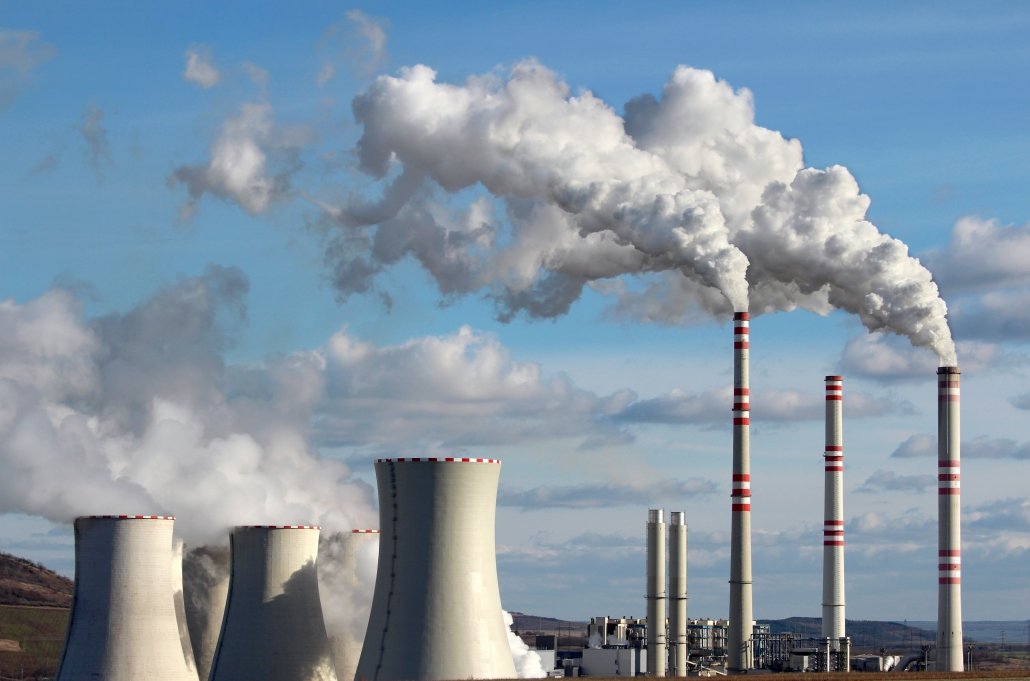
- Burning fossil fuels – When coal, oil and gas are burned, carbon dioxide is released into the atmosphere.

Emissions from a coal power plant
- Agriculture – Increased pastoral farming (animal husbandry) leads to more methane being released into the atmosphere.
- Dumping waste in a landfill – as waste decomposes, it releases methane.
- Agriculture – agricultural practices lead to the release of nitrogen oxides into the atmosphere.
Natural factors enhancing the greenhouse effect
In addition to human activities, natural processes also contribute to the enhanced greenhouse effect. These are:
- Orbital changes – Milankovitch cycles refer to variations in the Earth’s tilt and orbit around the Sun, resulting in natural warming and cooling periods.
- Volcanic eruptions – carbon dioxide is released into the atmosphere during eruptions.
- Solar output – the amount of radiation emitted by the Sun fluctuates. High levels of radiation lead to an increase in Earth’s temperatures.


